Introduction- Water is a precious resource. It is like an elixir for life. Without water the survival of living organisms cannot be imagined. Every year world water conservation day is observed on 22nd march. As per the, United Nations (U.N.) Guidelines an adult person should use an average 50 liters water /day for drinking, bathing, cleaning and washing etc. As the population is increasing there is demand of water for different chores of household activities. Water is required for agriculture, infrastructure development, industries, buildings etc.
About 71% of the earth is covered by water. It is present in oceans as salty water, rivers, lakes, ice caps, glaciers etc. Humans cannot simply use it. The fresh water present in rivers, lakes, ponds and underground water is useful to humans. Fresh water is only 2.5 % only. About 68% of this fresh water is found in polar ice caps, 30 % as underground water and about 2% water is found in rivers, lakes, soil water, atmospheric moisture, biological water in plants and animals. So, only 0.006 % of fresh water is available for human consumption. This too is being polluted.
In summer season, the water level goes deep down. In many parts of India and the World there is scarcity of water.
Forms of Water-
1. Solid Forms of water- Ice and snow
2. Liquid Forms of water- Liquid water
3. Gaseous forms of water- Atmospheric moisture, clouds
Sources of Water-
The sources of water can be categorized into surface water and Underground water.
Surface water is the water found in ponds, lakes, and rivers. It is either flowing or remain stagnant in water bodies. In Polar Regions, this water remains in form of snow, icebergs or floating chunks of ice. A portion of surface water that flows without getting collected is called run-off water. It causes leaching of minerals and soil-erosion. Run-off water also forms the ponds and lakes. A portion of surface water percolates inside the soil to form the underground water.
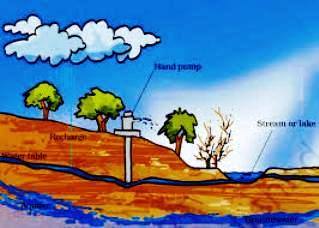
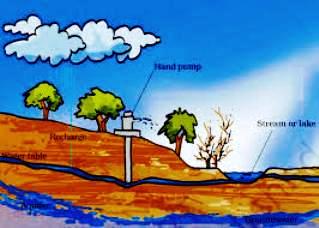
The seepage of surface water deep in the soil to form underground water is called as percolation or infiltration. The uppermost layer of the underground water is called water table. The underground water stored in between two layers of rocks is called as aquifer. The water table varies from place to place. It is used for differ purposes by humans and taken up by the hand pump, tube-well and well etc. Less rainfall and less percolation of water result in lowering down of water table. In summer season it is particularly common.
Reasons of depletion of water table-
1. Increasing Population- The population is increasing day by day. The present population of the world is 7.8 billion and is projected to reach 9.9 billion by 2050. India is second most populated country of the world. Its present population is 1,380004385 as per UN data. It is 17.7 % of the world population. India ranks 7th in terms of total land area.
The increasing population requires more water. This water is used for drinking, bathing, cleaning, washing etc. It is mainly taken from the underground water through well, tube-well, hand-pump etc. So, the water table is going down.
2. Increasing Industrial activities- Water is used in different kind of products making by industries. Water bottling plants, cold drink making companies, food processing units, iron-ore industries etc. use the underground water. So, water table is gradually going down. This becomes more problematic during summer season.
3. Increasing agricultural activities- The agriculture is entirely dependent on water. At least one or two times irrigation is necessary for the normal growth, development, flowering , fruiting etc like physical and physiological activities. Extensive agriculture is the form of agriculture which requires more and more land area to do cultivation. It is to get more crop yield. Intensive agriculture is also for getting maximum crop yield. But, it done at the same crop field by more improved technology like –high yielding seed (hybrid seeds), regular irrigation, green house making, use of fertilizers, pesticides etc is done to get maximum crop production. It uses underground water also. So, there is depletion of water table.
| S.N. | WATER BASED ACTIVITY | PERCENTAGE OF WATER USED |
| 1 | Agriculture | 67 % |
| 2 | Household Activities | 9 % |
| 3 | Water supply | 8 % |
| 4 | Electricity generation | 7 % |
| 5 | Manufacturing of Goods | 4 % |
| 6 | Mining | 2 % |
| 7 | Other Activities | 3 % |
Distribution of water in India and the World-
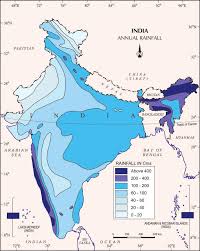
The distribution of water across the world is not even. The water is in plenty where excess rainfall occurs. The water is very little in those areas which receive scanty rainfall. In India, the distribution of water is quite different. Some areas receives plenty of rainfall while some areas very less rainfall. Floods are common in those areas which receive excessive rainfall. In such areas water table is high. Droughts are common in those areas which receive little rainfall. In such areas water table is low. The north-east parts of India and Western Ghats receives above 400 cm. of rainfall per year. The dry and desert areas like Rajasthan receive very less rainfall. Excess rainfall results into flood while scanty rainfall results in drought. The people face problems in both situations. The mismanagement of water is also a factor causing flood and less availability of water in different parts of the world.
Water Management– Water is very precious. The wastage of water occurs knowingly or unknowingly at individual level and mass level. The supply of drinking water occurs from well-planned pipe system. But, due to leakage at some places water does not reach to its destination. Leaking taps, overflow of tanks in houses etc. are some of wastage of water at individual level.
The flowing of rainwater to water bodies like rivers, lakes and non utilization of rainwater by humans is also wastage of water. The rainwater can be used to recharge the underground water. This is called as rainwater harvesting or water harvesting.
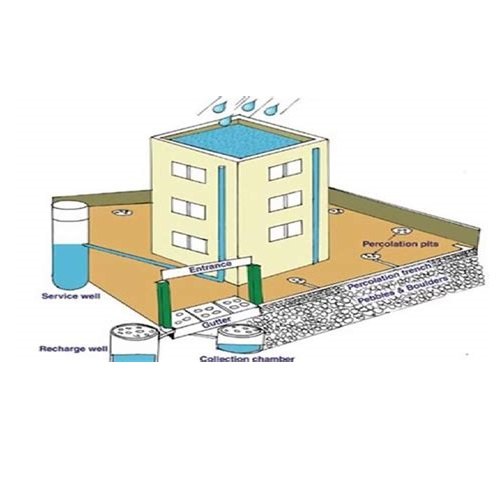
Rainwater Harvesting
In old times the water was collected from bawadies or step wells. The roof-top water harvesting is the best way to collect the rain water. In Rajasthan people make bunds (wall to check the rain water) in low laying sloppy areas.
Our Role in water conservation– We use water for our daily uses. Sometimes it is wasted knowingly or unknowingly. So, we can conserve by doing following activities at our level-
(a) Turn off the tap while brushing.
(b) Mop the floor instead of washing
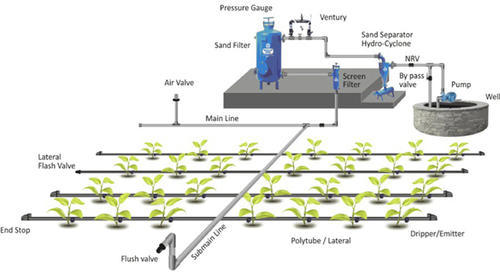
(c) Use of modern water irrigation methods like drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation methods
Effect of water scarcity on plants-Water is essential for plants to do photosynthesis, transpiration and other physiological activities. In absence of continuous rainfall and irrigation, plants start wilting. Their leaves go down. They turn pale in colour. Eventually, they dry out. So, irrigation at regular interval is necessary. During water absorption from the soil the plants also absorb the minerals.
EXERCISE QUESTIONS-
Q.1 Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(a) The freshwater stored in the ground is much more than that present in the rivers and lakes of the world.
(b) Water shortage is a problem faced only by people living in rural areas.
(c) Water from rivers is the only source for irrigation in the fields.
(d) Rain is the ultimate source of water.
Ans- (a) T (b) F (c) F (d) F
Q.2 Explain how groundwater is recharged?
Ans-The water from rainfall and water from water bodies like rivers, ponds, lakes etc. seeps down in the soil and fill the spaces deep below the ground. This process is called infiltration. Thus, infiltration of water recharges the groundwater.
Q.3 There are ten tube wells in a lane of fifty houses. What could be the long term impact on the water table?
Ans-If the tube wells are working for long time then the underground water will be reduced and water table will go down.
Q.4 If you have been asked to maintain a garden. How will you minimize the use of water?
Ans- The two modern methods of irrigation are –drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation methods. They save the water from wastage. In drip irrigation, water is supplied at the base of roots and in sprinkler water is supplied by sprinklers. Thus, optimum water will be used to maintain the garden.
Q.5 Explain the factors responsible for depletion of water table.
Ans- Following are the factors responsible for depletion of water table.
1. Increasing Population- The population is increasing day by day. The present population of the world is 7.8 billion and is projected to reach 9.9 billion by 2050. The increasing population requires more water. This water is used for drinking, bathing, cleaning, washing etc. It is mainly taken from the underground water through well, tube-well, hand-pump etc. So, the water table is going down.
2. Increasing Industrial activities- Water is used in different kind of products making by industries. Water bottling plants, cold drink making companies, food processing units, iron-ore industries etc. use the underground water. So, water table is gradually going down. This becomes more problematic during summer season.
3. Increasing agricultural activities- The agriculture is entirely dependent on water. At least one or two times irrigation is necessary for the normal growth, development, flowering , fruiting etc like physical and physiological activities. Extensive agriculture is the form of agriculture which requires more and more land area to do cultivation. It is to get more crop yield. Intensive agriculture is also for getting maximum crop yield. But, it done at the same crop field by more improved technology like –high yielding seed (hybrid seeds), regular irrigation, green house making, use of fertilizers, pesticides etc is done to get maximum crop production. It uses underground water also. So, there is depletion of water table.
4. Uneven distribution of water- The distribution of water across the world is not even. The water is very little in those areas which receive scanty rainfall. Droughts are common in those areas which receive little rainfall. In such areas water table is low. So, little rainfall indirectly causes depletion of water table.
5. Non-management of water-The run-off water can be harvested by making chekdams or watershed harvesting. The rainwater harvesting can help in water conservation and increasing water table. Absences of such management strategies indirectly cause depletion of water table.
Q.6 Fill In the blanks with the appropriate answers:
(a) People obtain groundwater through ………….. and ……….
(b) Three forms of water are ……….., ……………..and ……………
(c) The water bearing layer of the earth is ………………….
(d) The process of water seepage into the ground is called …………………
Ans-
(a) Wells, hand pumps
(b) solid, liquid, gas (or vapour)
(c) aquifer
(d) infiltration
Q.7 Which one of the following is not responsible for water shortage?
(i) Rapid growth of industries
(ii) Increasing population
(iii) Heavy rainfall
(iv)Mismanagement of water resources
Ans-(iii) Heavy rainfall
Q.8 Choose the correct option. The total water-
(i) in the lakes and rivers of the world remains constant.
(ii) under the ground remains constant.
(iii) in the sea and oceans of the world remains constant.
(iv) of the world remains constant.
Ans-(iv) of the world remains constant.
Q.9 Make a sketch showing groundwater and water table. Label it.
Ans-