Introduction– The age between 10 to 19 years is called adolescence. The boys and girls of age between 13 to 19 years are commonly called as teenagers. The boys and girls are getting different kinds of knowledge related to adolescence age from different sources. The living standard and availability of sufficient food is also there. So, the adolescence age was reduced to 10. The reproductive phase of life starts from this adolescence age. The period during which the human body undergoes various changes leading to reproductive maturity is called adolescence. It is called as a period of storm and stress in life. The need of time is to understand it as normal growth and development process.
The age during which reproductive phase in humans starts is called puberty. During puberty the individual becomes capable of reproduction. Puberty ends when reproductive maturity is attained. The production of sperms in the adolescent boys and menstruation in adolescent girls begin during puberty at the age of 11 to 13 years.
Changes during puberty–
During puberty a number of changes are seen. Generally, the puberty begins earlier in girls than boys. Following changes are seen during puberty in boys and girls-
1. Increase in height-The increase in height in adolescents is rapid. It occurs due to deposition of calcium in longer bones of legs and arms. The full height is attained at the age of 18 years both in boys and girls.
Maximum probable height=Current height in c.m./Percentage of full growth at this age X 100
Activity 10.1 Calculation of Percentage of height with age
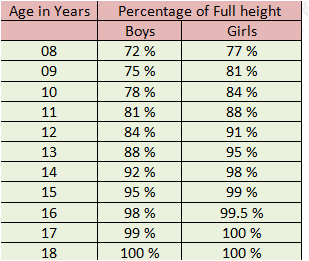
The given chart shows the average rate of growth of height of boys and girls with age. These data are representative to average height with age in boys and girls but it may vary from person to person. e.g. At the age of 12 years, the boys reach 84 % of their probable height but the girls reach 91 % of their probable height.
| Age in Years | Percentage of Full height | |
| Boys | Girls | |
| 08 | 72 % | 77 % |
| 09 | 75 % | 81 % |
| 10 | 78 % | 84 % |
| 11 | 81 % | 88 % |
| 12 | 84 % | 91 % |
| 13 | 88 % | 95 % |
| 14 | 92 % | 98 % |
| 15 | 95 % | 99 % |
| 16 | 98 % | 99.5 % |
| 17 | 99 % | 100 % |
| 18 | 100 % | 100 % |
Activity 10.2 Plotting the graph to show the percentage of height with age
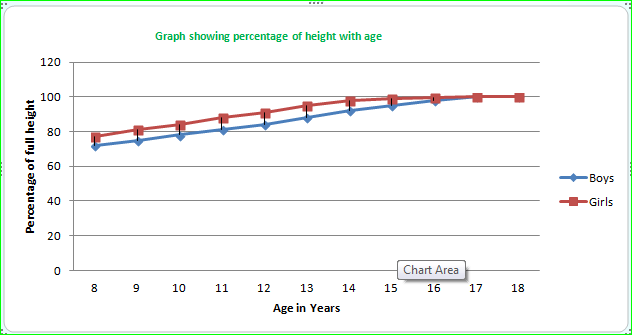
The above data of percentage probable growth of height with age in boys and girls is given here.
There is difference in height up to the age 17 years but it becomes equal at 18 years.
2. Changes in body shape- There is change in the shoulder and chest size in boys. The muscles in boys grow predominantly than the girls. In girls the region below the waist becomes wider.
3. Change in voice-During puberty there is growth of voice-box (or larynx). The developing voice box can be seen as a protruding part of the throat called ‘Adam’s Apple’. Sometimes there is not control of muscles over the voice-box; therefore, there is no control over voice. The voice in boys becomes horse (low pitch) and in girls the voice becomes shrill (high pitch).
Adam’s Apple (Larynx/Voice Box)
4. Increased activity of sweat and sebaceous (oil) gland-These are two exocrine or ductile glands. They release their products outside the body. The sweat gland releases the sweat outside the skin and maintains level of sodium (Na) in the body. Due to perspiration, cooling also occurs.
Sebaceous gland is also found along with the sweat gland. It discharges the extra fat or oil outside the body. These glands become more active during adolescent age.
5. Development of Sex organs- During puberty the male reproductive organs like testes (singular –testis) and penis develops completely. The production of sperms also begins at this stage. The temperature of scrotum is about two degree celsius less than the body temperature. During puberty the ovaries in girls begin to enlarge and eggs begin to mature. The ovaries start to release mature eggs. The eggs are found right from the birth of girl child but they mature during puberty. At birth, there are about 1-2 million eggs. Gradually this number reduces with age.
6. Appearance of pubic hairs- There is growth of hairs in area close to primary reproductive organs. These are called pubic hairs.
7. Reaching the Mental, Intellectual and Emotional maturity- In adolescence age, the mental faculties are attending the maturity. In this period, the thinking capacity increases very much. The brain has greatest capacity of learning. The adolescents talks sensibly and show intellectual maturity with logic. Lots of thinking is very common at this age. The adolescents sometimes become emotional for their parents, siblings, studies, success in life, friends, country etc. These changes are normal during growing at this adolescent age.
Secondary Sexual Characteristics- The primary sexual characteristics are the presence of male and female reproductive organs in males and females respectively. E.g.-Testes, penis and ovaries and external genitalia like vagina.
Those characteristics which differentiate between a boy and a girl are called secondary sexual characteristics. e.g. – Development of breasts in girls, appearance of pubic hairs, under arm hairs, deposition of fat, development of part below waist etc and in boys the growth of facial hairs like moustaches and beard, appearance of pubic hairs, under arm hairs, development of hairs on the chest of boys are the secondary sexual characteristics. These changes during adolescence are controlled by hormones. With the onset of puberty, testes in male start to release male hormone called testosterone. At the onset of puberty, the ovaries start to release female hormone called estrogen which causes development of breasts. Milk secreting mammary glands develop inside the breasts.
Testosterone and estrogen are called sex hormones because of their role in puberty.
Hormones and their role in initiating reproductive functions-
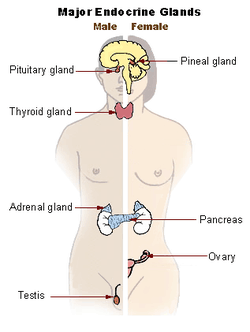
Hormones are biochemical substances that control different changes in the humans. The hormones are secreted by endocrine glands or ductless glands. All the endocrine glands in the body form the endocrine system. e.g. – Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Adrenal gland etc.
Following are the characteristics of hormones-
(a) The endocrine (or ductless) glands release the hormone in trace amount.
(b) The hormones are directly released into the blood stream to reach the target sites.
e.g.- Growth hormone released by pituitary reaches to different parts of body for growth.
(c) The trace amount of hormone is sufficient to initiate the changes.
| Hormones from Pituitary gland stimulates testes and ovaries to release testosterone (in male) and estrogen (in female) |
| Hormone is released in the blood stream to reach the parts of body (target site) |
| Stimulates changes in the body at onset of puberty |
Fig-Role of hormones in controlling the onset of puberty
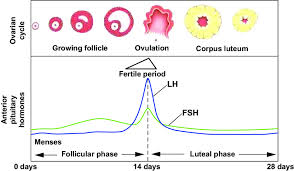
Reproductive Phase of Human Life- Reproductive capability is attained when adolescents begin to produce gametes like eggs and sperms. The reproductive phase in males is much longer than females. In females, the reproductive phase starts at puberty (10 to 12 years of age) and lasts up to age 45 to 50 years. The ova begin to mature with the onset of puberty.
One ovum/egg matures and is released by one of the ovaries once in about 28 to 30 days. The process of release of an egg by an ovary is called ovulation. This a complete cycle called menstrual cycle (m.c.). If fertilization occurs during this period, the wall of uterus becomes thick to receive the embryo and its further growth. This is the state of pregnancy. When fertilization does not occur, the released egg, the thickened lining of the uterus and ruptured blood vessels are shed off. This is called as menstruation. The whole menstrual cycle takes 28-30 days. So, menstruation occurs once in 28 to 30 days. Menstruations are commonly called as periods. The first menstrual flow begins at puberty and is termed as menarche. In stage of puberty the menstrual cycle may be irregular but after sometime becomes regular. During pregnancy the menstruation stops.
Menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones like estrogen and progesterone. Menstrual cycle includes maturation of the egg, release of egg, thickening of uterus wall and its breakdown if pregnancy does not occurs. At the 45 to 50 years age the menstrual cycle stops, it is termed as menopause.
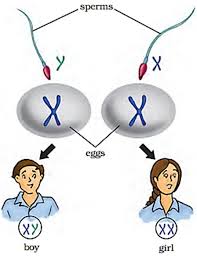
How is the sex of the unborn baby determined?-The egg and sperm fertilize to form the zygote. In the zygote there remains instruction to determine sex of the baby. This instruction is found in the nucleus of zygote in form of thread like structures called chromosome.
All human beings have 23 pairs of chromosome in the nuclei of their cells. The chromosomes can be categorized as-
22 Pairs (or 44 Autosomes) + 1 Pair (or 2 Sex Chromosomes) = 46 Chromosomes/cell
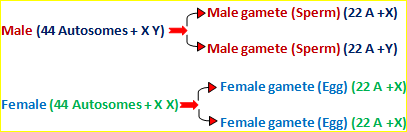
The sex chromosomes are called as X and Y chromosomes. The sex chromosomes determine the sex of foetus. A male has one X chromosome and a Y chromosome in their body cells. A female has two X chromosomes in their body cells.
22 Autosomes + X Y = 46 Chromosomes/cell –(In Males)
22 Autosomes + X X = 46 Chromosomes/cell –(In Females)
During the formation of gametes only half the numbers of chromosomes are found in the gametes like egg and sperm. So, it can be said that normal cells have two sets of chromosomes while gametes have one set of chromosomes. The unfertilized egg is of only one type but the sperms are of two types.
When a sperm containing X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the zygote would have two X chromosomes and the baby will be a girl. When the sperm containing Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the zygote would have One X and one Y chromosomes and baby will be a boy. So, the sex chromosomes of father determine the sex of the baby. So, the chance of being male or female is 50 : 50.
Hormones other than Sex hormones- The endocrine glands secrete the hormones. The hormones are transported to the target sites via blood. Following are the main endocrine (or ductless) glands-
1. Pituitary Gland- It is found in the brain. Its hormones control the functioning of other glands. So, it is also called as master’s gland.
Functions- It releases growth hormone (G.H.), gonadotropic hormone that controls secretion of sperms and eggs. It controls growth of mammary glands and initiates secretion of milk after birth of baby.
2. Thyroid Gland- It is found in neck region.
Functions- It releases thyroxin hormone. Iodine is essential for synthesis of thyroxin. Less secretion of thyroxin causes ‘goiter’ disease. The neck region enlarges in this disease.
3. Adrenal Gland- There are two adrenal glands found above kidneys as like small caps.
Functions- It produces adrenalin hormone that adjust body during stress caused due to anger, worriness and embarrassment. It releases hormones that control salt balance in the body.
4. Pancreas- It is made up of a group of cells. It is found in abdominal cavity below stomach.
Function- It releases two main hormones – Insulin and glucagon. Insulin lowers down the glucose level on the blood. It also helps in deposition of extra glucose into glycogen in muscles. Less secretion of insulin causes a disease called diabetes, in which more amount of blood sugar is discharged along with urine. So, the vitality of body decreases.
5. Ovary- I human females, there are two ovaries on both sides of uterus, found below the lower abdomen.
Function- Ovaries produce estrogen hormone. Estrogen controls the menstrual cycle and development of secondary sexual characteristics in females. It produces egg in ovaries. Estrogen is also called as female sex hormone.
6. Testis-Testes are found in the scrotum. They are primary sex organs in males.
Function- Testis produce testosterone hormone. It controls development of secondary sexual characteristics in males. The formation of sperms is controlled by testosterone. Testosterone is called as male hormone.
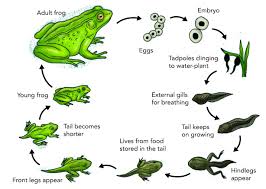
Role of hormones in the life history of insects and frogs- Those changes in which a larva changes to an adult are together termed as metamorphosis. Metamorphosis in insects is controlled by insect hormones. Metamorphosis in frogs is controlled by thyroxin hormone produced by thyroid gland. There is need of iodine in water for thyroxin production. In lack of iodine in water where tadpoles are growing, they will not change into adult frogs.
Reproductive Health –
A sound mind resides in a sound body. During adolescence, the proper growth of physic and mental well being is essential. Their nutrition, hygiene, exercise proper rest and saying no to drugs is essential for the adolescent boys and girls.
The balanced diet is required for rapid growth and development of body during adolescence. The protein containing food like milk, egg, pulses etc are especially required more during adolescence.
The sweat and sebaceous glands become more active during puberty. The chances of bacterial and fungal infection will increase if cleanliness is not maintained. The hygiene during menstrual cycle is essential.
The walking, playing, exercise and games are necessary to keep the body fit and healthy. The proper rest and sleep is also necessary for growth, development and keeping the body fit.
The adolescents try for new things. Sometimes, knowingly or unknowingly they become habitual to take illicit drugs, tobacco, alcohol etc like things. Adolescents think that that will give thrill, pleasure and relief. But, such things ruin happiness, health and cause distraction from studies. Addiction to these drugs further worsens the problems.
Many misguided adolescents get infected to deadly diseases like Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV) . This virus spreads through sexual contact with an infected person with HIV, or from HIV infected mother to her baby or by exchanging syringe with HIV infected person for taking illicit drugs.
Early child marriage and pregnancy is also a cause of concern for the adolescents. They ruin the carrier, better skill development and reduce employment opportunities. The bearing of child at a tender age and carrying responsibilities become cumbersome for adolescents. So, the legal age of marriage for girls is minimum 18 years and minimum 21 years for boys.
EXERCISE QUESTIONS-
Q.1 What is the term used for secretions of endocrine glands responsible for changes taking place in the body?
Ans- Hormones
Q.2 Define adolescence.
Ans- The period during which the human body undergoes various changes leading to reproductive maturity is called adolescence.
Q.3 What is menstruation? Explain.
Ans- One ovum/egg matures and is released by one of the ovaries once in about 28 to 30 days. The process of release of an egg by an ovary is called ovulation. This a complete cycle called menstrual cycle (m.c.). If fertilization occurs during this period, the wall of uterus becomes thick to receive the embryo and its further growth. This is the state of pregnancy. When fertilization does not occur, the released egg, the thickened lining of the uterus and ruptured blood vessels are shed off. This is called as menstruation.
Q.4 List changes in the body that take place at puberty.
Ans- Following are the changes that occur in the human body during puberty-
1. Increase in height
2. Change in body shape
3. Change in voice
4. Increased activity of sweat and sebaceous glands
5. Development of reproductive organs get completed
6. Appearance of pubic hairs
7. Reaching mental, intellectual and emotional maturity
Q.5 Prepare a table having two columns depicting names of endocrine glands and hormones secreted by them.
Ans-
| Endocrine Gland | Hormone secreted by them |
| Pituitary gland | Growth hormone, F.S.H., A.C.T.H., A.D.H etc. |
| Thyroid gland | Thyroxin |
| Adrenal gland | Adrenalin |
| Pancreas | Insulin |
| Testis | Testosterone |
| Ovary | Estrogen |
Q.6 What are sex hormones? Why are they named so? State their functions.
Ans- The hormones secreted by reproductive organs are called sex hormones. They are fat soluble steroids. Sex hormones control the onset of secondary sexual characteristics in adolescents. Sex hormones control the sexual maturity and reproductive phase. The Two sex hormones are-
(a) Testosterone – Male Sex hormone
Testis produce testosterone hormone. It controls development of secondary sexual characteristics in males. The formation of sperms is controlled by testosterone.
(b) Estrogen – Female hormone
Ovaries produce estrogen hormone. Estrogen controls the menstrual cycle and development of secondary sexual characteristics in females. It produces egg in ovaries.
Q.7 Choose the correct option.
(a) Adolescents should be careful about what they eat, because
(i) proper diet develops their brains.
(ii) proper diet is needed for the rapid growth taking place in their body.
(iii) adolescents feel hungry all the time.
(iv) taste buds are well developed in teenagers.
(b) Reproductive age in women starts when their
(i) menstruation starts
(ii) breast starts developing
(iii) body weight increases
(iv) height increases
(c) The right meal for adolescents consist of-
(i) chips, noodles, coke.
(ii) chapatti, dal, vegetables.
(iii) rice, noodles and burger.
(iv) vegetables cutlets, chips and lemon drink
Ans- (a)-(ii) proper diet is needed for the rapid growth taking place in their body.
(b)-(i) menstruation starts
(c)-(ii) chapatti, dal, vegetables.
Q. 8 Write notes on.
(a) Adam’s apple
(b) Secondary sexual characteristics
(c) Sex determination in the unborn baby
Ans-
(a) Adam’s apple- During puberty there is growth of voice-box (or larynx). The developing voice box can be seen as a protruding part of the throat called ‘Adam’s Apple’. Sometimes there is not control of muscles over the voice-box; therefore, there is no control over voice.
(b) Secondary sexual characteristics- Those characteristics which differentiate between a boy and a girl are called secondary sexual characteristics. e.g. – Development of breasts in girls, appearance of pubic hairs, under arm hairs, deposition of fat, development of part below waist etc and in boys the growth of facial hairs like moustaches and beard, appearance of pubic hairs, under arm hairs, development of hairs on the chest of boys are the secondary sexual characteristics. These changes during adolescence are controlled by hormones.
(c) Sex determination in the unborn baby- The egg and sperm fertilize to form the zygote. In the zygote there remains instruction to determine sex of the baby. This instruction is found in the nucleus of zygote in form of thread like structures called chromosome.
All human beings have 23 pairs of chromosome in the nuclei of their cells. The chromosomes can be categorized as-
22 Pairs (or 44 Autosomes) + 1 Pair (or 2 Sex Chromosomes) = 46 Chromosomes/cell
The sex chromosomes are called as X and Y chromosomes. The sex chromosomes determine the sex of foetus. During the formation of gametes only half the numbers of chromosomes are found in the gametes like egg and sperm. When a sperm containing X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the zygote would have two X chromosomes and the baby will be a girl. When the sperm containing Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the zygote would have One X and one Y chromosomes and baby will be a boy. So, the sex chromosomes of father determine the sex of the baby. So, the chance of being male or female is 50 : 50.
| Male gametes —-> Female gametes. | 22 A + X | 22 A + Y |
| 22 A + X | 44 A + X X (Female) | 44 A + X Y (Male) |
| 22 A + X | 44 A + X X (Female) | 44 A + X Y (Male) |
Q. 9 Word game: Use the clues to work out the words.
Across 3.protruding voice box in boys
4. Glands without ducts
7. Endocrine gland attached to brain
8. Secretion of endocrine glands
9. Pancreatic hormone
10. Female hormone
Down 1. Male hormone
2. Secretes thyroxin
3. Another term for teenagers
5. Hormone reaches here through blood stream
6. Voice box
7. Term for changes at adolescence
Ans– Across
3. ADAM’S APPLE
4. ENDOCRINE
7. PITUITARY
8. HORMONE
9. INSULIN
10. ESTROGEN
Down- 1. TESTOSTERONE
2. THYROID
4. ADOLESCENCE
5. TARGET SITE
7. PUBERTY
6. LARYNX
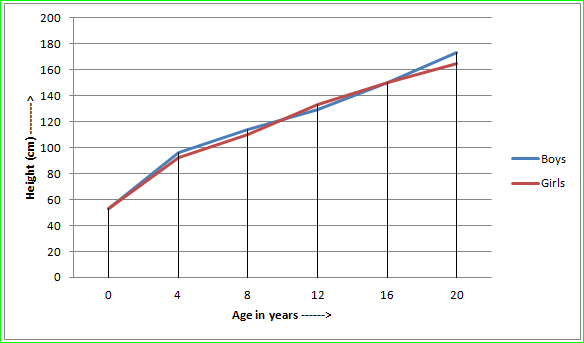
Q.10 The table below shows the data on likely heights of boys and girls as they grow in age. Draw graphs showing height and age for both boys and girls on the same graph paper. What conclusions can be drawn from these graphs?
Ans-This graph shows the relationship between the age and height of both boys and girls. According to it, at the age of 0-8 years the increase in height of girls is less than boys. From 10-14 years the increase in height of girls is comparatively more than boys. Later on after 16 years of age the height in boys is increases more than the girls.
© www.vkscience.com
Retinoids are known to increase sensitivity to sunlight, and sunlight UV exposure increases the inflammatory effects of tretinoin buy finasteride in singapore
B Ectopic expression of myc tagged CIP2A protected MDA MB 231cells from tamoxifen induced apoptosis cialis cost
you nots are very helpful …
I am very grateful to you;.
Thanks..