Aim-Preparation and analysis of Pedigree Charts of any one of the genetic traits such as rolling of tongue, blood groups, ear lobes, widow’s peak and colour blindness in a selected special family.
Principle– The Mendelian concept of dominance and segregation can also be studied in humans by preparing and then analyzing the pedigree charts. The internationally approved symbols for indicating males and females, marriages, various generations (I, II, III), etc., are given below.
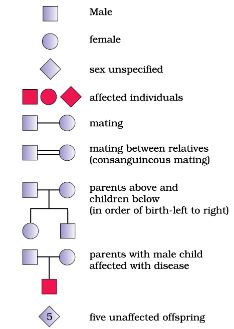
Requirements– Information about characters/traits in a family for more than one generation
Procedure– Select a family in which any one of the monogenic traits such as tongue rolling, widow’s peak, blood groups’, red-green colour blindness, dimples in the cheek, hypertrichosis of ear, hitch-hiker’s thumb, etc., is found. Ask the person exhibiting the trait to tell in which of his/her parents, grandparents (both maternal and paternal), their children and grand children the trait in question is present. Among surviving individuals the trait may also be examined. The information made available is the basis for the preparation of pedigree chart using the appropriate symbols. A careful examination of the pedigree chart would suggest whether the gene for the character is autosome linked dominant or recessive, X – chromosome linked dominant or recessive, Y- chromosome linked or not.
Explanations-
7(a)1. Autosome Linked Dominant traits/Autosomal dominant trait-These are the traits whose encoding gene is present on any one of the Autosomes. The pedigree-chart can be of the given below pattern where the female is exhibiting the trait-
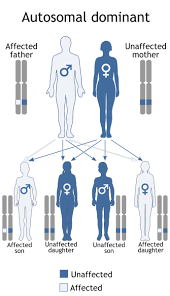
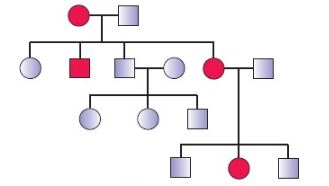
The characteristic features of inheritance of such type of traits are –
(a) Transmission of traits occurs from parents of either sex.
(b) Males and females are equally affected.
(c) The pedigree is vertical, i.e., the trait is marked to be present in each of the generations.
(d)Multiple generations are characteristically affected.
e. g.- Brachydactyly, Polydactyly, Dimple in the cheek , Myotonic Dystrophy, rolling of tongue, ABO blood groups, widow’s peak, free hanging ear lobes etc.
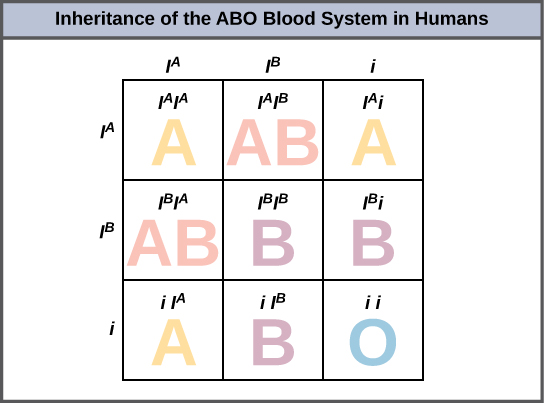
Rolling of tongue is an autosomal dominant trait. It affects men and women at an equal rate. Therefore, it can be said that trait is associated with automsomal chromosomes but not with X or Y chromosomes. ABO blood types are due to three different alleles of a single chromosome. A person has two types of alleles only. So, the type of blood group is due to multiple allelism and co-dominance.
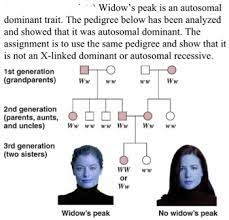
Widow’s peak is a hairline that protrudes in the middle, forming a peak. It can be in males as well as in females. The opposite of a widow’s peak is a straight hairline. Widow’s peak is an autosomal dominant trait two dominant alleles or one dominant and one recessive allele. The straight hairline is an autosomal recessive trait, meaning that people with a straight hairline must inherit two recessive alleles.
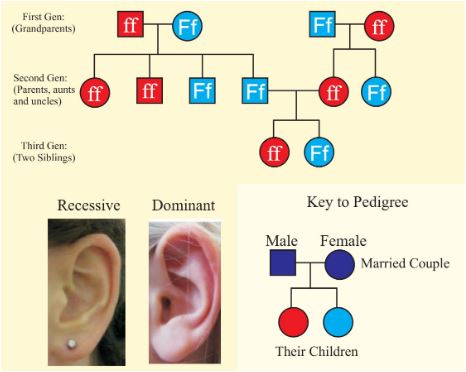
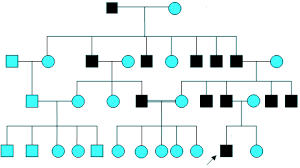
7 (b) 2. Autosomal Recessive trait/Autosome linked recessive trait– These are the traits whose mutant allele is recessive to its wild type allele. The pedigree chart can be more or less of the pattern given below where the lady (marked by the arrow) is showing the albanism trait.
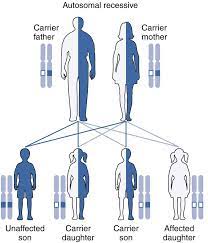
The following are the salient features of the inheritance of such type of traits.
(a) Occur in equal proportions in multiple male and female siblings, whose parents are normal but carriers;
(b) The siblings are homozygous for the defective allele, but their parents, though some may appear normal, are obviously heterozygous, i.e., are merely carriers of the trait.
(c) Consanguinity (marriage between man and woman genetically related to each other, such as cousins) occasionally results in the appearance of such traits.
e. g. -Albanism, Sickle Cell Anemia, Attached Ear lobes etc.
Courtesy: https://www.vedantu.com/
7(c) 3. X-Linked Dominant traits– These are the traits whose encoding gene is present on the X- chromosome, and the mutant allele of which is dominant over its wild-type allele. Such traits are very rare, and are almost difficult to find in the population. e.g. -Oral-facial-digital syndrome (Duchene Muscular Dystrophy), which results in absence of teeth, cleft (bifid) tongue associated with mental retardation. The pedigree chart may appear as –
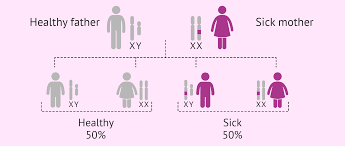
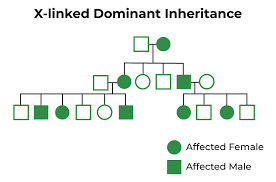
The characteristics of such inheritance are:
(a) The trait appears in almost all the generations, and the inheritance is vertical.
(b) If the female is affected, then about half of her sons are affected.
(c) If the male is affected then all of his daughters would be affected, but none of his sons are affected. (d) In short, the pedigree resembles the pattern of inheritance of autosomal dominants, except that there is no male-to-male transmission.
7(d) 4. X-linked Recessive traits– These are the traits whose encoding gene is present on the X-chromosome and its mutant allele is recessive to its wild-type allele. e. g.- Red-green colour blindness, Hemophilia etc.
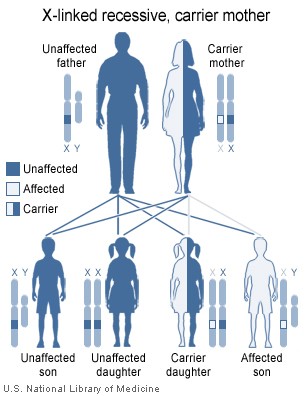
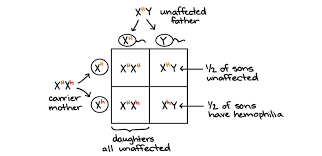
The characteristic features of such inheritance are:
(a) Females express the trait only when they are homozygous for the mutant allele, whereas the males do so even when they are hemizygous for it. The pedigree chart would appear as-
b) About half of the sons of the carrier (heterozygous for the trait) females are affected. In case of homozygous females showing the trait, fifty percent of her daughters and all of her sons are likely to be affected. Therefore, the males are most affected in the population.
(c) Affected persons are related to one another through the maternal side of their family.
(d) Any evidence of male-to-male transmission of the trait rules out the X- linked inheritance.
7(e) 5. Y-chromosome linked traits-These are the traits whose gene is present on the Y-chromosome. The females do not have any Y-chromosome, whereas all the males must have a Y-chromosome to be a male, and this Y-chromosome they get from their father. Therefore, any trait linked to the Y- chromosome must be present only in males. This is why these traits are also called male-sex limited traits. All the sons of the affected male would express the trait whereas none of his daughters would do so. The pattern of the pedigree chart would be as-
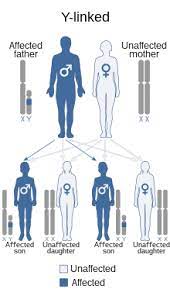
e.g.- Hypertrichosis of the ear (presence of hairs on pinna), Flatfoot characteristics, Hair loss etc.
Disclaimer: This article is compiled from different sources. We owe a deep sense of gratitude for the individual works, pictures taken from different sites. Please let us know if any shortcoming is there.