KEY CONCEPTS– Chemical Reaction, Reactants, Products, Notations or symbols of physical states of reactants and products, Types of chemical reactions, Combination Reaction, Decomposition Reaction, Displacement Reaction, Reactivity series of metals, Double Displacement Reaction, Exothermic reactions, Endothermic reactions, Balanced chemical equations, Precipitation reaction, Oxidation Reaction, Reduction Reaction, Oxidizing and reducing agents, Effects of oxidation reactions in daily life, Redox reactions, Corrosion, Rusting, Rancidity,
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-7606197531762322"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
CHEMICAL REACTION– The process in which two or more substances react to give new substances having different properties is known as a chemical reaction. The chemical reaction is written in form of a word chemical equation. The word chemical equation does not give true picture of a chemical reaction. The chemical reaction is written in form of symbol equation.
e.g.- Carbon + Oxygen Carbon dioxide [word chemical equation]
C + O2 CO2 [symbol equation]
On the left hand side of the arrow, reactants are written and on the right hand side of the arrow products are written. The direction of arrow decides the position of reactants and products. Some chemical reactions are balanced by writing equal number of atoms of reactants and products. All chemical reactions take place at N.T.P. (Normal Temperature and Pressure) conditions i.e. at 273 K temperature and 1 atmospheric pressure.
REACTANTS-The substance which react in a chemical reaction are called as reactants. e.g.- Carbon and oxygen are reactants in the above reaction.
PRODUCTS-The substance which is formed as a result of a chemical reaction is known as a product. The product may be one or more. The properties of products are quite different from their reactants.
e. g.- The carbon dioxide formed in the above reaction has quite different properties than carbon and oxygen.
NOTATIONS OR SYMBOLS FOR PHYSICAL STATES OF REACTANTS AND PRODUCTS-The chemical reactions are written in form of symbols of their reactants and products. It helps in balancing of atoms of reactants and products of chemical reactions. The physical states are also written in a chemical reaction to make it more informative. The symbols of physical states are changed into italics to differentiate them from reactants and products symbols and the notation or symbol used for solids is (s), for liquids is (l), for gases is (g) and for aqueous solutions is (aq.). The gas evolved in a chemical reaction can be shown by an upward arrow ( ). The solid precipitate formed in a chemical reaction can be written by (ppt.). Dilute solvents are written as (dil.) and concentrated as (conc.).
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS– On the basis of ways of exchange of partners to form product, the chemical reactions are broadly categorized into following four types.
(a) COMBINATION REACTION-The reactions in which two or more reactants combine to form a single substance under suitable conditions are called combination reaction.
e. g.- C (s) + O2 (g) — Sunlight——> CO2 (g)
e. g.- H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) —-Heat—–> 2 HCl (g)
(b) DECOMPOSITION REACTION- The chemical reactions in which a single compound splits into two or more simple substances under suitable conditions are called decomposition reactions.
e. g.- 2 H2O (l) —Electrolysis—-> 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g)
e.g.- 2AgCl (s) —–Sunlight—-> 2 Ag (s) + Cl2 (g)
e.g.- ZnCO3 (s) —-Heat——> ZnO (s) + CO2 (g)
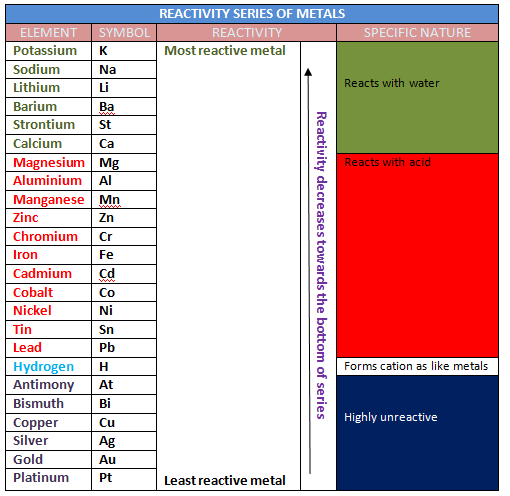
(c) DISPLACEMENT REACTION-The chemical reactions in which one element takes the position of other element in a compound by displacing it, are called displacement reaction reactions. The reactivity of one metal over the other metal decides the displacement reaction.
© www.vkscience.com
e. g.-Ag NO3 (aq.) + Cu (s) ———–> Cu(NO3)2 (aq.) + 2Ag (s)
e.g.- H2SO4 (aq.) + Zn (s) ———–> ZnSO4 (aq.) + H2 (g)
(d) DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION- The chemical reactions in which one component each of both the reacting molecules get exchanged to form the products are called as double displacement reactions.
e.g. BaCl2 (aq.) + Na2 SO4 (aq.) ———–> BaSO4 (s) + NaCl (aq.)
Barium sulphate
(White Precipitate)
e.g.- NaCl (aq.) + AgNO3 (aq.) ————-> NaNO3 (aq.) + AgCl (s)
EXOTHERMIC AND ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS-Those chemical reactions, in which heat is liberated, are called as exothermic reactions. The container in which exothermic reaction occur gets heated up. e. g.- 3 H2 (g) + N2 (g) ——->2 NH3 (g) +92 kJ
NaOH (aq.) + HCl (aq.) ———> NaCl (aq.) + H2O (aq.) + 57.5 kJ
Combustion and respiration are also exothermic reactions.
Those chemical reactions, in which heat is absorbed, are called as endothermic reactions. The container in which endothermic reaction occur gets cold. e. g.-
C(s) + H2O (g) ———-> CO (g) + H2 (g) -130kJ
N2 (g) + O2 (g) ———–> 2 NO (g) -180kJ
BALANCED CHEMICAL EQUATIONS-A chemical equation in which the number of atoms of each type of element is equal on both sides of the arrow is called a balanced chemical equation. In a balanced chemical reaction the total mass of reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. Balancing of a chemical reaction is done according to the law of conservation of mass. According to this law the mass can neither can be created nor can be destroyed in a chemical reaction. There is no change in mass of reactants and the products.
The balancing of a chemical reaction or the mass balancing can be done in following steps-
1. Write the chemical equation in form of a word equation. The reactants are kept on left and products on right hand side. There is + (plus sign) between two or among more reactants are there. Similarly, there is + (plus sign) between two or among more products. Reactants and products are separated by an arrow pointing towards products.
2. The word equation is changed into symbol equation, by writing symbols and formulae of all the reactants and products.
3. The atoms of reactants and products are balanced. The formulae of substances will remain unchanged. By keen observation, the coefficients are adjusted on both sides to maintain law of conservation of mass. Count the number of atoms of both side and adjust them.
e.g.- Methane burns to produce carbon dioxide gas and water.
or, Methane + Oxygen ——-> Carbon dioxide + Water [Word chemical equation]
or, CH4 + O2 ——> CO2 + H2O [Symbol Equation]
or, CH4 + 2 O2 ——> CO2 +2 H2O [Balanced Chemical Equation]
PRECIPITATION REACTION-The chemical reaction in which a precipitate (an insoluble salt) is formed is called as precipitation reaction. The precipitate is represented by a symbol (ppt.).
e.g.- Ca(OH)2(s) + CO2 (g) ——–> CaCO3 ( ppt. ) + H2O (l)
e.g.- AgNO3(aq.) +NaCl (aq.) —-> AgCl (s) + NaNO3(aq.)
(White ppt.)
e.g.- BaCl2 (aq.) + Na2SO4 (aq.) ——> BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq.)
(White ppt.)
OXIDATION REACTION– The chemical reaction in which there is loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen by any reactant is called as oxidation reaction. {Old concept}
It is also defined as the chemical reaction in which an atom, molecule or ion looses one or more electrons. {Electronic Concept}

e. g.- 2Cu (s) + O2 (g) ——–> 2 CuO (s) {Cu is oxidized to CuO}
e.g.- N2H4 + O2 ———> N2 + 2 H2 O { O2 is reduced to H2O}
Hydrazine
REDUCTION REACTION– The chemical reaction in which there is gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen by any reactant is called as oxidation reaction. {Old concept}
It is also defined as the chemical reaction in which an atom, molecule or ion gains one or more electrons. {Electronic Concept}
e.g.- ZnO (s) +H2 (g) ———> Zn (s) + H2O (l)
e.g.- Cl2 (g) + H2 (g) —–Sunlight—> 2HCl (g)
OXIDISING AND REDUCING AGENTS– The reactants that brings about the oxidation is called as oxidizing agents. Oxidizing agents are themselves get reduced in a chemical reaction. The reactants that bring about the reduction are called as reducing agents. Reducing agents are themselves get oxidized in a chemical reaction.
e.g.- Oxygen, ZnO, Chlorine etc are oxidizing agents.
e.g.- Hydrogen, Copper, Hydrazine etc are reducing agent.
The electron loosing species (atom or molecule or ion) is called as reducing agent while electron gaining species is called as oxidizing agent. ‘X’ is a reducing agent while ‘Y’ is an oxidizing agent.
e. g.- Iron is losing electrons to oxygen, therefore iron like metal is an example of reducing agent. Oxygen is accepting electrons from iron, therefore, oxygen like non-metal is an example of oxidising agent.
EFFECTS OF OXIDATION REACTIONS IN DAILY LIFE–
Following are the common effects of oxidation reaction in our daily life.
(i) The cellular respiration inside our body cells ours due to oxidation.
(ii) The burning of fuels for cooking, running of vehicles of fossil fuels are due to oxidation.
(iii) Corrosion is slow oxidation of some metals. It is an uneconomical chemical process causing loss of metals.
(iv) Rancidity of edible food items is an oxidation process that make them unfit for eating.
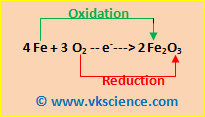
REDOX REACTIONS– The chemical reaction in which both oxidation and reduction occurs simultaneously is called as redox reaction. In a redox reaction, one reactant loses certain electrons (i.e. undergoes oxidation) and other reactant gains electrons (i.e. undergoes reduction)
e. g. -4 Fe + 3 O2 ——–> 2 Fe2O
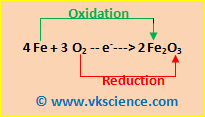
e.g.- CuO + H2 ——> Cu + H2O
CuO——–> Cu {Reduction}
H2 ———-> H2O {Oxidation}
In this reaction, iron is oxidized and oxygen is reduced. The oxidation number of iron has increased and oxidation state of oxygen has reduced.
CORROSION-The slow oxidation of some metals in the presence of air and moisture is called as corrosion reaction. Corrosion is an oxidation reaction. Corrosion is usually seen in iron, copper, silver, brass, steel etc. In case of iron, it is called as rusting. Rusting occurs in presence of oxygen and moisture i.e. water vapours. Near sea shores the rate of rusting increases. Rusting causes great economic loss as the bridges, iron objects, vehicles etc get rusted gradually. Alloy formation, galvanization, chromium plating, applying paint, oil and grease are common methods to prevent rusting.
Iron + Oxygen + Moisture ——-> Rust
Fe + O2 + H2O ——-> Fe2O3.xH2O
In rust, iron forms hydrated iron (III) oxide.
The copper utensils often get coated with a dull green coating. This coating is a mixture of copper hydroxide and copper carbonate.
Copper + Oxygen + Water vapour + Carbon dioxide –> copper hydroxide + copper carbonate
Or, Cu + O2 + H2O + CO2 ——-> Cu (OH) 2 + CuCO3
The silver develops a black coating in moist and polluted areas. The polluted air contains Sulpher which combines with silver to form silver sulfide (Ag2S). Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas contains Sulpher.
Silver + Hydrogen Sulfide + Oxygen + Water Vapour –> Silver sulfide + Hydrogen
Or, 2 Ag + H2S + O2 + H2O —> Silver sulfide (Ag2S) + H2
All the above are example of corrosion in iron, copper and silver metals. So, the corrosion tarnishes the metals. Applying of oil, paint, grease, galvanization, alloy formation, chromium plating etc. are some of the methods of preventing rusting.
RANCIDITY-The chemical reaction in which food items are oxidized resulting into production of foul smell and taste is called rancidity. The oil and fats found in the oily foods are more prone to rancidity. e.g.- Milk and curds become rancid if left overnight in summer season.
Prevention of rancidity-
(a) Adding of antioxidants to oily food substances.
(b) Keeping foods in air tight containers.
(c) Keeping the food in nitrogen filled packets or in liquid nitrogen.
(d) Keeping food item at low temperature in refrigerators.
IN-TEXT (WITHIN THE CHAPTER)
Q.1 Why should magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning?
Ans-Magnesium is a reactive metal. When magnesium is kept in air for a long time, a layer of magnesium oxide (MgO) is formed on its surface. The magnesium metal reacts with oxygen of air, to form magnesium oxide. When flame is brought near the magnesium ribbon having coating of magnesium oxide, it does not catch fire easily. Therefore, the surface of magnesium ribbon should be properly cleaned with sand paper before burning of it in air.
Q.2 Write the balanced equations for the following chemical reactions:
(i) Hydrogen + Chlorine Hydrogen chloride
(ii) Sodium + Water Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
(iii) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
Ans–
(i) H2 + Cl2 2 HCl
(ii) 2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2
(iii) 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 3BaSO4 + 2AlCl3
Q.3 Write the balanced equations with state symbols for the following reactions:
(i) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
(ii) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride (in water) and water.
Ans–
(i) BaCl2 (aq.) + Na2SO4 (aq.) ——> BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq.)
(White ppt.)
(ii) NaOH (aq.) + HCl (aq.) ———> NaCl (aq.) + H2O (l)
Q.4 A solution of the substance ‘X’ is used for white washing.
(i) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance ` X` with water.
Ans.–
(i) The substance `X` is calcium oxide (also called as quick lime). It’s formula is CaO.
(ii) CaO(s) + HO (l) Ca(OH) (s)
‘X’ Calcium Hydroxide
Q.5 With the help of an experiment, show that in the electrolysis of acidulated water, the volume of one gas is twice the volume of the other gas. Name the gas.
Ans-The gas released in twice volume by the electrolysis of acidulated water is hydrogen.
2H2O (aq.) —Electrolysis—-> 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
Q.6 Why does the colour of copper sulphate change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Ans– When an iron nail is dipped into the copper sulphate solution, a reddish brown coating of copper is acquired by it due to displacement reaction.
CuSO4 (aq.) + Fe (s) ——–> FeSO4 (aq.) + Cu(s)
Iron nail Copper deposited on iron nail
Q.7 Give an example of double displacement reaction.
Ans– BaCl2 (aq.) + Na2 SO4 (aq.) ———–> BaSO4 (s) + NaCl (aq.)
Barium sulphate
(White Precipitate)
Q.8 Identify the substances that are oxidized and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions:
(i) 4 Na (s) + O2 (g) ——> 2 Na2O (s)
(ii) CuO (s) + H2 (g) ——> Cu (s) + H2O (l)
Ans– (i) In this reaction, Sodium (Na) is oxidized to Sodium oxide (Na2O). So, Oxygen (O2) is reduced.
(ii) In this reaction, Copper (II) oxide (CuO) is reduced to copper (Cu). So, Hydrogen is oxidized to water (H2O).
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-7606197531762322"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
EXERCISE QUESTIONS
Q. 1 Which of the following statements about the reaction given below are incorrect?
2 PbO (s) + C (s) ————> 2 Pb (s) + CO2 (g)
(a)Lead is getting reduced. (b) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidized.
(c) Carbon is getting oxidized. (d) Lead oxide is getting reduced.
(i) a and b both are incorrect
(ii) a and c
(iii) a, b and c
(iv) all are incorrect.
Ans– (i) a and b both are incorrect
It is because lead is getting oxidized to PbO in backward direction. CO2 is getting reduced to C in backward direction.
Q.2 Fe2 O3+ 2Al ———> Al2 O3 + 2 Fe
The above reaction is an example of:
(a) Combination reaction (b) Double displacement reaction
(c) Decomposition reaction (d) Displacement reaction
Ans-(d) Displacement reaction
Aluminium lies above Iron in the reactivity series of metals. Since, Al is replacing Fe from Fe2 O3. Therefore it is an example of displacement reaction.
Q.3 What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings? Tick the correct answer:
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(b) Chloride gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c) No reaction takes place.
(d) Iron salt and water are produced.
Ans- (a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
Fe (s) + 2HCl (dil.) ———> FeCl2 (aq.) + H2 (g)
This reaction is an example of displacement reaction.
Q.4 What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Ans- A chemical equation is said to be balanced if- (a) atoms of different elements on both sides of equation are equal and (b) the equation is molecular i.e., molecules of reactants and products are written.
Balancing of a chemical reaction is done according to the law of conservation of mass. According to this law the mass can neither can be created nor can be destroyed in a chemical reaction. There is no change in mass of reactants and the products.
Q.5 Transfer the following into chemical equations and balance them.
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and Sulpher dioxide.
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Ans-
(a) H2 + N2 ——-> NH3
or, 3 H2 + N2 ——->2 NH3
(b) H2S + O2 ———> H2O + SO2
or, 2 H2S + 3 O2 ———> 2 H2O + 2 SO2
(c) BaCl2 (aq.) + Al2(SO4)3 (aq.) ———–> BaSO4 (s) + AlCl3 (aq.)
Barium sulphate
or, 3 BaCl2 (aq.) + Al2(SO4)3 (aq.) ———–> BaSO4(s) + NaCl (aq.)
Barium sulphate (ppt.)
(d) K + H2O ——> KOH + H2
or, 2 K + 2 H2O ——> 2 KOH + H2
Q.6 Balance the following chemical equations:
(a) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 ———-> Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4————-> Na2SO4 + H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 ————–> AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 ———> BaSO4 + HCl
Ans-
(a) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 ———-> Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
| Element | No of atoms in reactants(L.H.S.) | No of atoms in products(R.H.S.) |
| H | 3 | 2 |
| N | 1 | 2 |
| O | 5 | 7 |
| Ca | 1 | 1 |
So, 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 ———-> Ca(NO3)2 + 2 H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4————-> Na2SO4 + H2O
| Element | No of atoms in reactants(L.H.S.) | No of atoms in products(R.H.S.) |
| H | 3 | 2 |
| S | 1 | 1 |
| O | 5 | 5 |
| Na | 1 | 2 |
So, 2 NaOH + H2SO4————-> Na2SO4 + 2 H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 ————–> AgCl + NaNO3
| Element | No of atoms in reactants(L.H.S.) | No of atoms in products(R.H.S.) |
| Na | 1 | 1 |
| Cl | 1 | 1 |
| Ag | 1 | 1 |
| N | 1 | 1 |
| O | 3 | 3 |
So, NaCl + AgNO3 ————–> AgCl + NaNO3
It is already a balanced chemical reaction.
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 ———> BaSO4 + HCl
| Element | No of atoms in reactants(L.H.S.) | No of atoms in products(R.H.S.) |
| Ba | 1 | 1 |
| Cl | 2 | 1 |
| H | 2 | 1 |
| S | 1 | 1 |
| O | 4 | 4 |
So, BaCl2 + H2SO4 ———> BaSO4 + 2 HCl
Q.7 Write the balanced equations for the following reactions.
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide ————> Calcium carbonate + water
(b) Aluminium + Copper Chloride ———-> Aluminum chloride + Copper
(c) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate ———–> Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
(d) Zinc + Silver nitrate ——–> Zinc nitrate + Silver
Ans–
(a) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 ——–> CaCO3 + H2O
(b) 2 Al + 3 CuCl2 ———-> 2 AlCl3 + 3Cu
(c) BaCl2 + K2SO4 ———–> BaSO4 + 2KCl
(d) Zn + 2 AgNO3 ———–> Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
Q.8 Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of reaction:
(a) Potassium bromide (aq.) + Barium iodide (aq.) —-> Potassium iodide (aq.) + Barium bromide (aq.)
(b) Zinc carbonate (s) ——-> Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide (g)
(c) Hydrogen (g) + Chlorine (g) ———> Hydrogen chloride (g)
(d) Magnesium (s) + Hydrochloric acid (aq.) ———–> Magnesium chloride (aq.) + Hydrogen (g)
Ans-
(a) 2 KBr (aq.) + BaI2 (aq.) ———> 2KI (aq.) + BaBr2 (aq.) – double displacement reaction.
(b) ZnCO3 (s) ———-> ZnO (s) + CO2 (g) –decomposition reaction
(c) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) ——–> 2HCl (g)-combination reaction
(d) Mg(s) + + 2HCl (dil.) ———> MgCl2 (aq.) + H2 (g)-displacement reaction
Q.9 What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Ans-Those chemical reactions, in which heat is liberated, are called as exothermic reactions. The container in which exothermic reaction occur gets heated up. e. g.-
3 H2 (g) + N2 (g) ——->2 NH3 (g) +92 kJ
NaOH (aq.) + HCl (aq.) ———> NaCl (aq.) + H2O (aq.) + 57.5 kJ
Those chemical reactions, in which heat is absorbed, are called as endothermic reactions. The container in which endothermic reaction occur gets cold.
e. g.-
C(s) + H2O (g) ———-> CO (g) + H2 (g) -130kJ
N2 (g) + O2 (g) ———–> 2 NO (g) -180kJ
Q.10 Why respiration is considered as an exothermic reaction?
Ans– Respiration releases energy in form of A.T.Ps in the cell. The oxygen breaks down the glucose
with the help of enzymes as a result carbon dioxide gas, water vapours and energy is released.
C6H12O6 (s) +6 O2 (g) ——–> 6CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l) +2820kJ
Q.11 Why are decomposition reactions called opposite to combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans– The chemical reactions in which a single compound splits into two or more simple substances under suitable conditions are called decomposition reactions.
e.g.- 2AgCl (s) —–Sunlight—-> 2 Ag (s) + Cl2 (g)
e.g.- ZnCO3 (s) —-Heat——> ZnO (s) + CO2 (g)
The reactions in which two or more reactants combine to form a single substance under suitable conditions are called combination reaction.
e. g.- C (s) + O2 (g) — Sunlight——> CO2 (g)
e. g.- H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) —-Heat—–> 2 HCl (g)
Since, there is breaking of substance in decomposition reaction whereas there is formation of any substance in combination reaction. Therefore, both reactions are called opposite to each other.
Q.12 Write equations for each decomposition reaction, where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity.
Ans-
(i) 2AgCl (s) —–Sunlight—-> 2 Ag (s) + Cl2 (g)
(ii)ZnCO3 (s) —-Heat——> ZnO (s) + CO2 (g)
(iii)2 NaCl ——Electricity—> 2Na + Cl2
Q.13 What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions?
Ans-The chemical reactions in which one element takes the position of other element in a compound by displacing it, are called displacement reaction reactions. The reactivity of one metal over the other metal decides the displacement reaction.
e.g.- H2SO4 (aq.) + Zn (s) ———–> ZnSO4 (aq.) + H2 (g)
The chemical reactions in which one component each of both the reacting molecules get exchanged to form the products are called as double displacement reactions.
e.g. BaCl2 (aq.) + Na2 SO4 (aq.) ———–> BaSO4 (s) + NaCl (aq.)
Q.14 In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement of copper metal. Write chemical equation involved.
Ans-The chemical reaction involved in refining of silver is-
Cu(s) +2AgNO3 (aq.) ——–Cu (NO3) (aq.) + 2Ag(s)
Q.15 What do you mean by precipitation reaction? Explain giving examples.
Ans– The chemical reaction in which a precipitate (an insoluble salt) is formed is called as precipitation reaction. The precipitate is represented by a symbol ( ) or as (ppt.).
e.g.- Ca(OH)2(s) + CO2 (g) ——–> CaCO3 ( ) + H2O (l)
e.g.- AgNO3(aq.) +NaCl (aq.) —-> AgCl (s) + NaNO3(aq.)
(White ppt.)
Q.16 Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples of each-
(a) oxidation (b) reduction
Ans–
(a) oxidation- The chemical reaction in which there is gain of oxygen by any reactant is called as oxidation reaction.
e. g.- 2 Zn (s) + O2 (g) ——-> 2 ZnO(s)
e. g.- 2Cu (s) + O2 (g) ——–> 2 CuO (s)
(b) reduction- The chemical reaction in which there is loss of oxygen by any reactant is called as reduction reaction.
e. g.- ZnO (s) +H2 (g) ———> Zn (s) + H2O (l)
e. g.- CuO (s) + H2 (g) ———–> Cu (s) + H2O (l)
Q.17 A shining brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element
‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Ans– The element ‘X’ is copper and the black coloured compound is copper (II) oxide.
2 Cu + O2 ——Heat———–> 2 CuO
‘X’ Copper oxide (Black)
Q.18 Why do you apply paint on iron articles?
Ans– Paints applied on the surface of iron articles cut off the direct contact of oxygen and moisture. Due to this protective coating the iron objects remain protected from the rusting.
Q.19 Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Ans- The chemical reaction in which oil and fats found in the oily food items are oxidized resulting into production of foul smell and taste of such food is called rancidity. The oil and fat containing food items when filled with nitrogen, stops rancidity i.e. oxidation of such food items as nitrogen is a non-reactive gas.
Q.20 Explain the following terms with one example of each- (a) Corrosion (b) Rancidity
Ans–
(a) Corrosion- The slow oxidation of some metals in the presence of air and moisture is called as corrosion reaction. Corrosion is an oxidation reaction. Corrosion is usually seen in iron, copper, silver, brass, steel etc. In case of iron, it is called as rusting. Rusting occurs in presence of oxygen and moisture i.e. water vapours. Near sea shores the rate of rusting increases. Rusting causes great economic loss as the bridges, iron objects, vehicles etc get rusted gradually. Alloy formation, galvanization, chromium plating, applying paint, oil and grease are common methods to prevent rusting.
Iron + Oxygen + Moisture ——-> Rust
Fe + O2 + H2O ——-> Fe2O3.xH2O
In rust, iron forms hydrated iron (III) oxide.
(b) Rancidity-The chemical reaction in which food items are oxidized resulting into production of foul smell and taste is called rancidity. The oil and fats found in the oily foods are more prone to rancidity.
e. g.- Milk and curds become rancid if left overnight in summer season.
§*****§
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-7606197531762322" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>