INTRODUCTION–
Living organisms have a limited lifespan. Unless they are not going to form new organism, they will finish. Their continuity of life will be lost. So, fertile organisms form new organism of same kind either by self or by the help of other individual of same species. The process of formation of similar types of organisms by existing organism is called reproduction.
There are two types of reproductions-
(a) Asexual Reproduction – New organism is formed by single parent. It is common in plants and animals.
(b) Sexual Reproduction- New organism is formed by two parents. It is common in plants and animals.
A. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS – New organism is formed by a single parent. It occurs by following methods-
1. Vegetative Propagation– The vegetative parts of plant is used to grow the new organism. e. g.- Roots in case of Sweet Potato and Mint, Stem in case of Strawberry and Chrysanthemum, Modified stem in case of Potato tubers, Leaves in case of Bryophyllum and African violet is used to develop new organism.
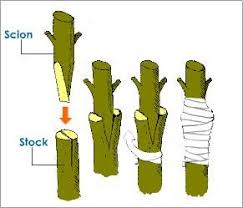
Vegetative Propagation also occurs by artificial methods like- Cutting, Grafting, Layering and Tissue culture. It is very useful for fruit yielding plants.
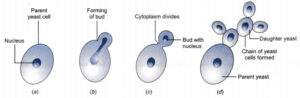
2. Budding– Bud is an asexual reproductive structure. This is an outgrowth of mother body in which a nucleus is found. The bud grows to form the new organism. e.g. – Yeast (A Fungus)
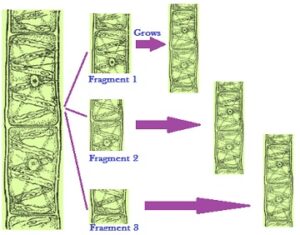
3. Fragmentation– Fragments are small asexual reproductive structures formed by fragmentation of mother body. Each fragment grows into a new organism. e. g.- Spirogyra
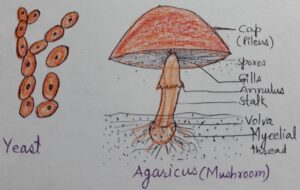
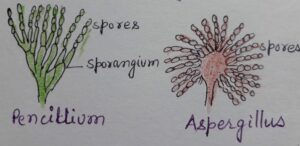
4.Spore Formation-Spores are small asexual reproductive structures that germinate to form new organism. Spores are formed in large number. They float in air and on finding suitable surface for germination, they form new organisms. The germinating surface must contain organic matter and water. e. g.- Ferns (Pteridophytes) and Fungi like Rhizopus, Mucor, Penicillium, Agaricus (Mushroom) etc.
B. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS- The reproduction in which two parents, one male and one female are required to form the new organism is called as sexual reproduction.
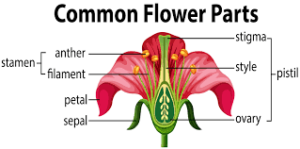
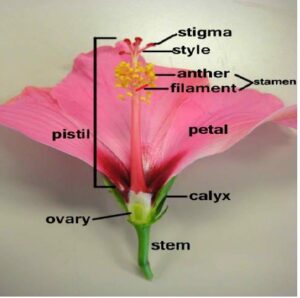
Uni-sexual and Bisexual Flowers– Those incomplete flowers which have either pistil or stamen are called uni-sexual flowers. e. g.-Papaya, Maize, Cucumber etc.
Those flowers which have both pistil as well as stamen are called as bisexual flowers. e. g.- Rose, china-rose, mustard, marigold, lotus etc.
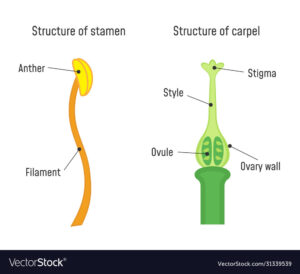
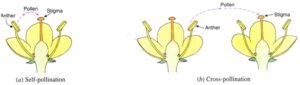
Pollination– The transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma is called pollination. There are two types of pollinations-
A. Self Pollination
B. Cross Pollination
When transfers of pollen grains occur from anther to the stigma of same flower, it is called as self pollination. When transfers of pollen grains occur from anther to the stigma of different flower, it is called as cross pollination.
On stigma, mature pollen grains germinate to form pollen tubes in which male gametes are found. The pollen tube moves below inside the ovary for fertilization.
Fertilization– The fusion of male gamete with female gamete to form zygote is called fertilization. As a result of fertilization, single celled zygote is formed.
Formation of Fruits and Seeds– As a result of fertilization some post-fertilization changes starts. The ovary changes into fruit and ovules change into seeds. So, fruit is ripened ovary.
Seed– The seed develops from the fertilized ovules. They have an outer protective covering called seed coat. Cotyledons are nutritive cells that give food to developing radical and plumule. The seed has either one cotyledon or two cotyledons. Single cotyledon containing seed is called monocotyledonous or monocot seeds. e.g.-Rice, wheat, grass etc. Two cotyledons containing seeds are called dicotyledonous or dicot seeds. e.g.-Pea. Gram, Mango etc.
Seed Germination– The seeds can remain in dormant stage for many months to many years. On finding suitable conditions, the seed germinate to form radicle and plumule. The small embryo develops into radicle and plumule. The root system develops from radicle and shoot system develops from plumule.
Seed Dispersal– The method of going of seed from one place to other by an agent is called seed dispersal. The agents to seed dispersal can be- air, wind, water, animals including humans, bats, explosion etc.
Some seeds have hairy structures and wings so they are carried away by wind to other place.
Exercise Questions
Q.1 Fill in the blanks.
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of the parent is called ……………..
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called ……..
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or of anther flower of the same kind is known as ……………….
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as …………………..
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of ……………., …………………. and ……………………
Ans – (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
Q.2 Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Ans- The following are different methods of asexual reproduction-
(i) Budding- Bud is an asexual reproductive structure. This is an outgrowth of mother body in which a nucleus is found. The bud grows to form the new organism. e.g. – Yeast (A Fungus)
(ii) Fragmentation-
(iii) Spore Formation-
Q.3 Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Ans- The reproduction in which two parents, one male and one female are required to form the new organism is called as sexual reproduction. As a result of sexual reproduction zygote is formed.
Q.4 State the main differences between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Ans-
| S.N. | ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION | SEXUAL REPRODUCTION |
| 1 | Only one parent is involved. | Two parents are involved. |
| 2 | Spores, Fragments, Buds like asexual structures are formed. | Seeds are formed. |
| 3 | It is a fast method of reproduction. | It is comparatively a slow method of reproduction. |
Q.5 Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Ans-
Q.6 Explain the differences between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Ans-
| S.N. | SELF -POLLINATION | CROSS-POLLINATION |
| 1. | When transfers of pollen grains occur from anther to the stigma of same flower, it is called as self fertilization. | When transfers of pollen grains occur from anther to the stigma of different flower, it is called as cross fertilization. |
| 2. | It occurs in bisexual flowers. | It usually occurs in unisexual flowers. |
| 3. | No genetic variation occurs. | Genetic variation occurs. |
- 7 How does the process of fertilization takes place in flowers?
Ans- The transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma is called pollination. On stigma, ripen pollen grains germinate to form pollen tube in which male gametes are found. The pollen tube moves through style to reach upto the ovary for fertilization. The pollen tube contains two male gametes. One of them fuses with egg to form zygote. The fusion of male gamete with female gamete (egg) to form zygote is called fertilization. As a result of fertilization, single celled zygote is formed.
Q.8 Match items in column I with those in column II:
Column I Column II
(a) Bud (i) Maple
(b) Eyes (ii) Spirogyra
(c) Fragmentation (iii) Yeast
(d) Wings (iv) Bread mould
(e) Spores (v) Potato
(vi) Rose
Ans- (a)- (iii) (b)- (v) (c)- (ii) (d)- (i) (e)- (iv)
Q.9 Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Ans- The natural method of going of seed from one place to other by an agent is called seed dispersal. The agents to seed dispersal can be-
(i) Wind- Some seeds like oak (Madar) seeds and cotton seeds have hairs on their seed coat. Some seeds like maple and drumsticks have wings and some others like seeds of grasses are very light. These seeds being hairy, winged and very light are carried away by the winds to distant places.
(ii) Water- Some seeds like coconut have fibrous outer coat that helps them to float on water. These seeds are dispersed by water.
(iii)Animals- Some seeds like xanthium have spiny seeds. They stick with the fur coat or tail of stray hairs.
(iv)Explosion etc.














where to buy cialis online safely Older African Americans and Latinos also showed increased drug arrest but not to the same extent as older whites