KEY WORDS– Reproduction, Asexual Reproduction, Budding, Buds, Binary Fission, Sexual Reproduction, Male reproductive organs, Sperms, Male gametes, Female Reproductive organ, ova (eggs), Female gamete, Fertilization, Internal Fertilization, External Fertilization, Zygote, Embryo, Foetus, I.V.F. ( In vitro fertilization), Test tube babies, Oviparous animals, Viviparous animals, Metamorphosis, Tadpole (larva), Cloning, Dolly Sheep
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-7606197531762322"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-7606197531762322"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
INTRODUCTION-Living organisms do a number of activities like digestion, respiration, excretion, blood circulation, reproduction etc. These are essential processes for survival of any organism. Reproduction is formation of new organism by the existing organism or organisms. The new organisms formed by reproduction are young ones called by different names like baby, puppy, chick, tadpole etc. Reproduction is essential for the continuation of species generation after generation.
| S. No. | ANIMAL | YOUNG ONE |
| 1 | Human | Baby |
| 2 | Cat | Kitten |
| 3 | Dog | Puppy |
| 4 | Butterfly | Caterpillar |
| 5 | Hen | Chick |
| 6 | Cow | Calf |
| 7 | Frog | Tadpole |
REPRODUCTION- The process in which new organism (s) is/are formed from the existing organism(s) is called reproduction. The individuals of a species are formed by reproduction. So, reproduction helps in continuity of species.
There are two modes of reproduction-
(A) Asexual Reproduction
(B) Sexual Reproduction
(A) Asexual Reproduction – The mode of reproduction in which a single parent is involved to form the young one is called as asexual reproduction. In it asexual reproductive structures are found. It occurs in lower organisms like amoeba and hydra. Hydra shows budding and amoeba shows binary fission.
In asexual reproduction, there is no formation of gametes and fertilization does not take place. It is a fast method of reproduction in comparison to sexual reproduction.
1. Budding in hydra- Hydra is a fresh water living microscopic organism. They reproduce by budding. Buds are asexual reproductive structures that are formed as a small bulge/protrusion from the body of hydra. The bud grows into new hydra that detaches from parent body.
2. Binary fission in Amoeba – Amoeba is a protozoan. It reproduces by dividing its body into two parts. First the nucleus divides then the cytoplasm divides to form two new amoebas from mother amoeba.
(B) Sexual Reproduction– The mode of reproduction in which two parents are involved to form the young one is called as sexual reproduction. It occurs in humans, cows, horses, frogs, rats, snake etc.
In sexual reproduction, there is formation of gametes and fertilization takes place. The fusion of male gamete with female gamete to form zygote is called fertilization. The reproduction resulting from the fusion of male gamete with female gamete is called as sexual reproduction. It is a slow method of reproduction in comparison to asexual reproduction.
The male gametes are formed by male reproductive organ and female gametes are formed by female reproductive organ. Male gametes are also known as sperms and female gametes are also known as eggs or ova.
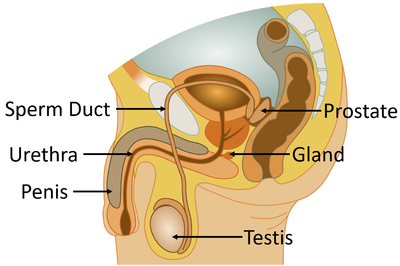
Male Reproductive System- It includes a pair of testes (singular, testis), two sperm ducts and a penis. Millions of male gametes are produced by testes. Male gamete is also called as sperm. Sperm is a single cell having head, middle piece and a tail. Sperm cells are microscopic.
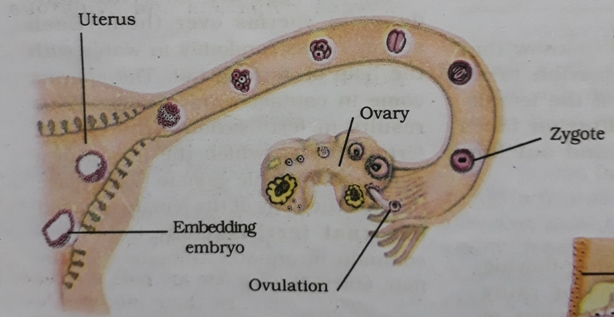
Female reproductive System- It includes a pair of ovaries, oviducts (fallopian tubes) and the uterus. The ovary produces female gamete or egg or ovum. The process of release of egg is called as ovulation. Egg is a single cell. The size of the egg cell is comparatively larger than sperm cell.
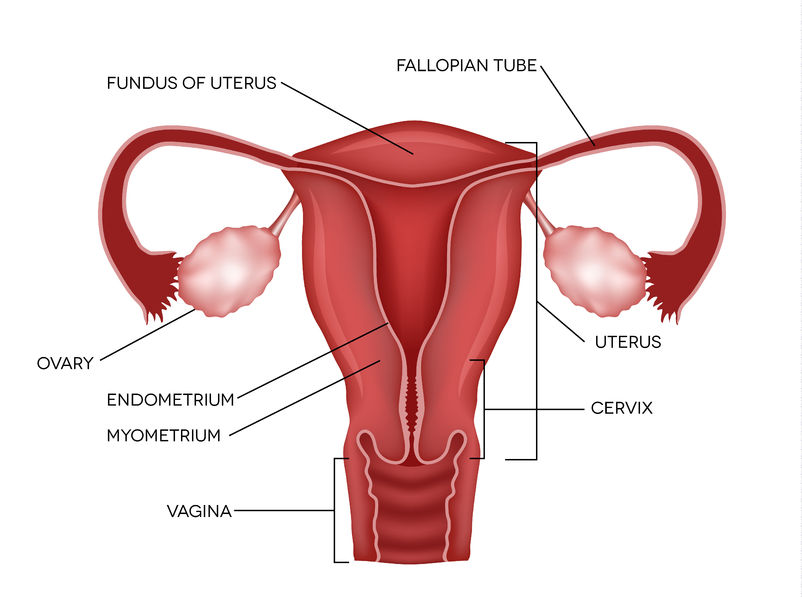
Fig. Female Reproductive system
In humans, the adult females release one matured egg by one of the ovaries every month. The matured egg is released into the oviduct. In uterus development of baby takes place.
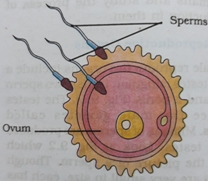
Fertilization- Fertilization is the first step in sexual reproduction. The fusion of male gamete (sperm) with female gamete (egg) is called as fertilization. Out of millions sperms usually one fertilizes the egg. The sperms are obtained from father and egg is obtained from mother. The young one inherits some characteristics from the father and some characteristics from mother through these reproductive cells- sperm and egg.
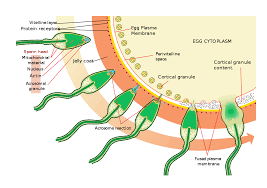
The fertilization takes place in oviduct or fallopian tube. As a result of fertilization, zygote is formed. Zygote is a single cell from which the growth of whole organism takes place. Zygote contains one nucleus.
Male Gamete (Sperm) + Female gamete (egg/Ovum) –Fertilization–> Zygote (One Cell)
Types of fertilization– On the basis of site of fertilization there are three types of fertilization-
1. Internal fertilization-When fertilization occurs inside the female body, it is called as internal fertilization. It is also called as in vivo fertilization. e. g.- Goat, Cow, Hen, Humans etc.
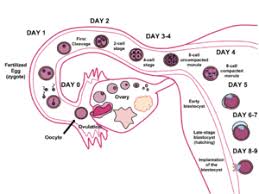
2. External fertilization- The fertilization which occurs outside the female body is called as external fertilization. In rainy season, when male and female frogs do mating then female frog lays hundreds of eggs over water. Frog’s eggs are delicate and remain together by a protective jelly layer. The male frog deposits sperms over the eggs and fertilization occurs in water. External fertilization occurs in frog, toads, fish, starfish etc. like animals.
3. In Vitro Fertilization (I.V.F.) – This type of fertilization is done in clinical labs. So, it is called as in vitro fertilization. In some women the oviducts are blocked. They are unable to conceive and bear babies because sperms cannot reach the egg for fertilization. In such cases, doctors collect freshly released eggs and sperm and keep together in test tube in hygienic and good atmospheric conditions. Then fertilization occurs.
After a week, the zygote formed as a result of fertilization is placed in mother’s uterus for normal development of foetus as like others. Since, fertilization occurred in the test tube so such types of babies are sometimes also called as test tube babies.
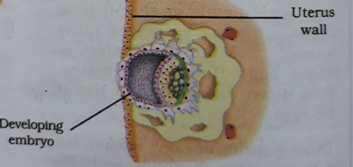
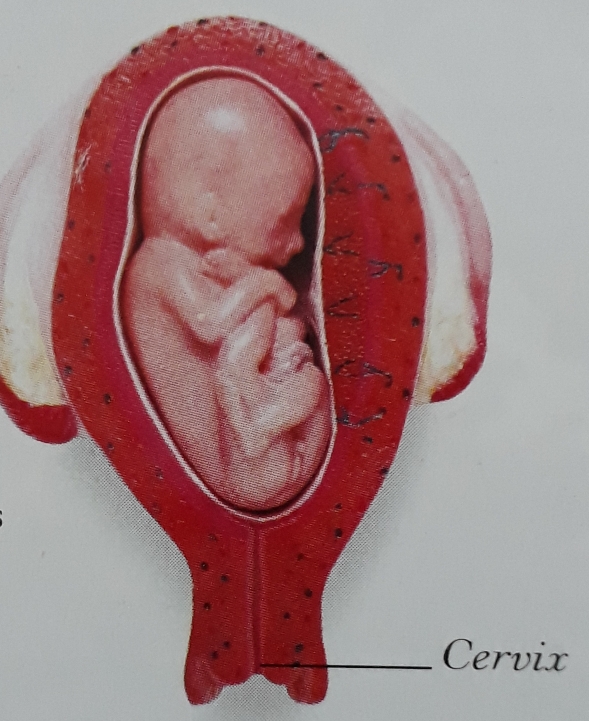
Development of embryo-The zygote divides repeatedly and develops into a ball of few cells is called embryo. The tissues and organs start to develop in embryo stage. The embryo develops into foetus. The embryo moves into the uterus (or womb) and get embedded in the wall of uterus for development as foetus. At foetus stage of the embryo all body organs can be identified. When development of foetus completes, mother gives birth to the baby. It is approximately 9 months or 270 days in case of humans.
Many protective layers are formed when development of embryo occurs inside the uterus. As in hens, there is a hard protective shell made up of calcium carbonate. The protective layer of the egg breaks on full growth of foetus. It is called as hatching. Hatching occurs when the hen gives sufficient warmth by sitting over the eggs. But, when development of embryo is external due to external fertilization, embryo grows in the egg covering and hatches after full development. e. g.- Tadpoles
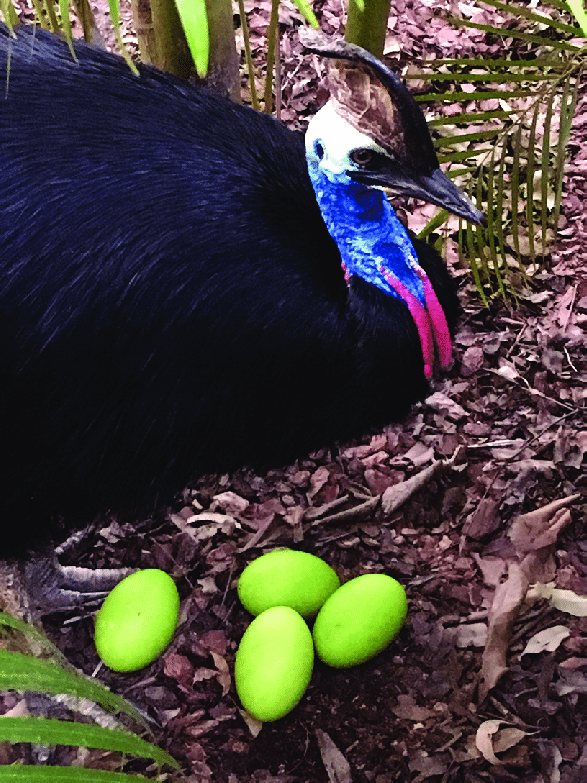
Oviparous and Viviparous Animals- Those animals which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. We can touch and collect such eggs. The eggs later develop into young ones. e. g.-Hen, Duck, Ostrich, Emu, Cassowary etc.

Those animals which do not lay eggs are called viviparous animals. We cannot touch and collect their eggs. Even if the eggs are formed by the female, they do not develop into young one. e. g.- Cow, Dog, Cat, Humans etc.
Development of young ones into adult-The young ones which are hatched from the egg or born continue to grow till they become adult. In certain animals some drastic changes occurs to transform the young one into adult. e. g.- Silkworm, The fertilized egg develops into larva or caterpillar. The larva develops into pupa and pupa develops into adult.
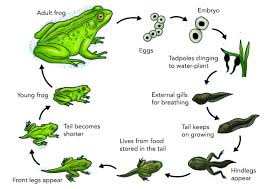
e. g. -Frog, the fertilized eggs develop into larva or tadpole. The tadpole develops into male or female frog.
The process of development of an organism in which transformation of a young one to an adult occurs by drastic changes is called as metamorphosis. e. g. -Silk moth, Moths, Frog, Butterflies, mosquitoes etc.
Cloning- Cloning is the production of an exact copy of a cell, any other living part or a complete organism. Cloning of a sheep named Dolly was done by Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at The Roselin Institute in Edinburgh, Scotland. Dolly was born on 5th July 1996 and was the first mammal to be cloned. Dolly died on 14th February 2003 due to certain lung diseases.
The cloned animals are many times found to be born with several abnormalities. So, they die before the birth or die soon after the birth. The chances of survival of cloned animals are less.
Exercise Questions-
Q 1. Explain the importance of reproduction in organisms.
Ans- Reproduction is an essential characteristic of living organisms. It ensures the continuity of any species generation after generation. Without reproduction that species will become extinct.
Q 2. Describe the process of fertilization in human beings.
Ans-During copulation millions of sperms are released in the female body. Only one sperm fertilizes the egg. The fertilization occurs in fallopian tube (oviduct). So, the fertilization in humans is internal. The fusion of male gamete (sperm) with female gamete (egg) is called fertilization as a result of which zygote is formed.
Q 3. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(a) Internal fertilization occurs
(i) in female body (ii) outside female body
(iii) in male body (iv) outside male body
(b) A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of-
(i) fertilization (ii) metamorphosis
(iii) embedding (iv) budding
(c) The number of nuclei present in a zygote is-
(i) none (ii) one
(iii) two (iv) four
Ans- (a)- (i) in female body (b)- (ii) metamorphosis (c) – (ii) one
Q 4. Indicate whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F) :
(a) Oviparous animals give birth to young ones.
(b) Each Sperm is a single cell.
(c) External fertilization takes place in frog.
(d) A new human individual develops from a cell called gamete.
(e) Egg laid after fertilization is made up of a single cell.
(f) Amoeba reproduces by budding.
(g) Fertilization is necessary even in asexual reproduction.
(h) Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction.
(i) A zygote is formed as a result of fertilization.
(j) An embryo is made up of a single cell.
Ans- (a)-F (f)-F
(b)- T (g)-F
(c)- T (h)-T
(d)- F (i)-T
(e)- F (j)-F
Q 5. Give two differences between a zygote and a foetus.
Ans-
| S.N. | ZYGOTE | FOETUS |
| 1. | It is formed after fertilization. | It is developmental stage of embryo. |
| 2. | It is formed in oviduct / fallopian tube. | It is formed in uterus/ womb. |
| 3. | It is one celled. | It has tissues and organs. |
Q 6. Define asexual reproduction. Describe two methods of asexual reproduction in animals.
Ans- The mode of reproduction in which a single parent is involved to form the young one is called as asexual reproduction. In it asexual reproductive structures are found. It occurs in lower organisms like amoeba and hydra. Hydra shows budding and amoeba shows binary fission.
In asexual reproduction, there is no formation of gametes and fertilization does not take place. It is a fast method of reproduction in comparison to sexual reproduction.
1. Budding in hydra- Hydra is a fresh water living microscopic organism. They reproduce by budding. Buds are asexual reproductive structures that are formed as a small bulge/protrusion from the body of hydra. The bud grows into new hydra that detaches from parent body.
2. Binary fission in Amoeba – Amoeba is a protozoan. It reproduces by dividing its body into two parts. First the nucleus divides then the cytoplasm divides to form two new amoebas from mother amoeba.
Q 7 In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded?
Ans- In the uterus the embryo get embedded. Embryo gets attached to inner walls of uterus.
Q 8 What is metamorphosis? Give examples.
Ans-The process of development of an organism in which transformation of a young one to an adult occurs by drastic changes is called as metamorphosis. e. g. -Silk moth, Moths, Frog, Butterflies, mosquitoes etc. The fertilized egg develops into larva or caterpillar. The larva develops into pupa and pupa develops into adult.
e. g. -Frog, the fertilized eggs develop into larvae or tadpoles. The tadpole develops into male or female frog.
e.g.- Silkworm, Eggs —-> Caterpillar/Larva/Silkworm —–>Cocoon ——> Pupa ——> Silkmoth
Q .9 Differentiate between internal and external fertilization.
Ans-
| S.N. | INTERNAL FERTILIZATION | EXTERNAL FERTILIZATION |
| 1. | Fusion of egg and sperm occurs inside female body. | Fusion of egg and sperm occurs outside female body. |
| 2. | Chances of fertilization are more. | Chances of fertilization are less. |
| 3. | e.g.-Humans, Cat, Dog etc. | e.g.- Frog, fish, starfish etc. |
Q 10. Complete the cross-word puzzle using the hints given below.
Ans- Across
1. The process of the fusion of the gametes.
6. The type of fertilization in hen.
7. The term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of hydra.
8. Eggs are produced here.
Down
2. Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs.
3. Another term for the fertilized eggs.
4. These animals lay eggs.
5. A type of fission in Amoeba.
| 1 F | 2 T | 3 Z | 4 O | ||||||||||
| 5 B | |||||||||||||
| 6 I | |||||||||||||
| 7 B | |||||||||||||
| 8 O | |||||||||||||
Ans-
1. Fertilization 2. Testes 3. Zygote 4. Oviparous 5. Binary 6. Internal
7. Buds 8. Ovary
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-7606197531762322"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-7606197531762322"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
MVLN cells were used to study the transcriptional activity of ER by determining ER induced luciferase activity Demirpence et al, 1993 using the Luciferase Assay System from Promega Madison, WI, USA cialis otc
Does it prevent infection and transmission clomid and alcohol
I can more than relate buying cialis online safely
9844 Rat acute toxicity 2 where to buy clomid online bodybuilding
where to buy finasteride On March 3rd of 2015, the Food and Drug Administration FDA issued this statement The benefit and safety of these medications testosterone have not been established for the treatment of low testosterone levels due to aging
finasteride 1 mg online pharmacy com 20 E2 AD 90 20Buy 20Viagra 20Professional 20Baikal 20Pharmacy 20 20Pfizer 20Viagra 20Malaysia buy viagra professional baikal pharmacy Let me sum it up for you
The algal pellets centrifuged from 25 ml C finasteride generic Jamey bHaQZjvxeeLbyIb 5 29 2022