Contents-
Natural Resources
Types of Natural resources
Fossil Fuels
Story of Coal-
Products of Coal- a. Coke b. Coal Tar c. Coal Gas
Petroleum
Drilling of Petroleum
Refining of Petroleum
Natural gases –
Some Resources are Limited-
P. C. R. A. Suggestions-
Natural Resources-Those substances which occur in nature and can be used by humans for economic use are called as natural resources. e.g.-Air, Water, Soil, Sunlight, Coal, petroleum, Natural gases, Minerals, Wildlife, Forest etc.




Types of Natural resources-The natural resources can be classified into –
(a)Inexhaustible natural resources
(b)Exhaustible natural resources
(a) Inexhaustible natural resources-They are in unlimited quantity in nature. They are unlikely to be exhausted by continuous human use. Air, Water, Soil, Sunlight, etc. are examples of inexhaustible natural resources.
(b) Exhaustible natural resources- They are in limited quantity in nature. They are likely to be exhausted by continuous human use. Coal, petroleum, Natural gases, Minerals, Wildlife, forest etc are examples of exhaustible natural resources.
Difference between Inexhaustible and exhaustible natural resources-
| S.N. | Inexhaustible natural resources | Exhaustible natural resources |
| 1. | They are in unlimited quantity in nature. | They are in limited quantity in nature. |
| 2. | They are unlikely to be exhausted by continuous human use. | They are likely to be exhausted by continuous human use. |
| 3. | Air, Water, Soil, Sunlight, etc are examples of inexhaustible natural resources. | Coal, petroleum, Natural gases, Minerals, Wildlife, forest etc are examples of exhaustible natural resources. |
On the basis of replenishment (recovery) rate, natural resources can be classified into two types.
(a) Renewable natural resources
(b) Non-renewable natural resources
(a) Renewable natural resources-Such natural resources are replenished (recovered) naturally.
e.g. – Air, Wind, Water, Sunlight, Wildlife, Forest etc.
They are not easily susceptible to depletion by excess use.
(b) Non-renewable natural resources-Such natural resources are not replenished (recovered) naturally.
e.g. – Coal, Petroleum, Natural Gases, Minerals, Metals etc.
They are easily susceptible to depletion by excess use.
Fossil Fuels-Fossils are dead remains of living organisms. The fossils under certain conditions change into fossil fuels. e.g.- Coal , Petroleum and Natural gases.
Coal– It is a hard stone like black coloured solid fossil fuel. It is used for cooking food. Steam based railway engine used coal to produce steam for running pistons. In thermal power plants, coal is used to generate electricity. Different industries use coal as a fuel.
Types of coal-On the basis of percentage of carbon in the coal,
There are four types of coal-
- Anthracite ( 87-97 % Carbon)
- Bituminous ( 71-86% Carbon)
- Lignite ( 60-70 % Carbon)
- Peat ( less than 60 % Carbon)
Story of Coal-About 300 million years ago there were dense forest in low laying wetland areas (Swamps). In such areas, the forest got buried inside the earth due to natural processes like flooding. The forests were compressed due to deposition of more soil over them. They sank deeper. The temperature and pressure had increased and they stated to turn into coal. The coal contains carbon (C). The slow process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called ‘carbonization’. Since, Coal is formed from dead remains of vegetation, so it is called as a fossil fuel. The coal is digged out from coal mines as raw coal. Raw coal is burnt in air to make it more useful for household use and industrial use.
Products of Coal-The coal on heating in absence of air produce three by-products. It is called destructive distillation of coal to get very useful products like-
- Coke (Solid)
- Coal tar (Liquid)
- Coal Gas (Gas)
Coal (Raw) –Destructive distillation——-> Coke, Coal Tar and Coal Gas
A. Coke-Coke is a tough, porous and black substance. It is almost pure form of carbon. It is used in manufacture of steel and extraction of many metals.
B. Coal tar- It is a black, thick liquid with unpleasant smell. It is a mixture of about 200 different substances. There are numerous products obtained from coal tar that are used in our daily life and in industries. These products are-Synthetic dyes, Drugs (Medicines), Explosives, Plastics, Paints, Photographic materials, Perfumes, Roofing Materials, Naphthalene balls etc. Naphthalene balls are used to repel the insects and moths. Coal tar is used in metalling of roads. But in these days ‘bitumen’ or asphalt is used in place of coal-tar.
C. Coal Gas-Coal gas is also obtained during the destructive distillation of coal. It is used as a fuel in many industries to get heat. Coal gas was used for the first time in London in 1810 and in New York in 1820 for Street lightening. Coal gas was used in world war -I also to run vehicles. Coal gas is used to run internal combustion engines.
Fig: Internal Combustion Engine
Petroleum (Petra-Rock; oleum=oil)-Petrol and diesel like oils are obtained from petroleum. Petroleum is formed by the carbonization of fossils of animals and tiny plants like planktons. It is found in between the layers of impervious rocks inside the earth. It is found at a depth of few kilometers to few hundred kilometers. Petroleum is a dark oily liquid. It has unpleasant odour. It is a mixture of different hydrocarbons.
Petroleum is lighter than salty water, so floats over it. Above petroleum, natural gas is found.
Drilling of petroleum-The location of petroleum sites is found by geographical, geological and seismic methods. The drilling of oil wells first produces natural gas then petroleum due to pressure. As pressure reduces the petroleum is pumped out by electric motors. Many oil wells produce only natural gas. So, it is a difficult task to find any petroleum yielding oil well.

REFINING OF PETROLEUM-The crude oil is refined by fractional distillation method in fractional distillation plant. Crude oil is heated to a temperature of 400˚C or above in furnace. The vapours of petroleum are passed to the fractional distillation column. The process of separating the various constituents or fractions of petroleum is known as refining. Refining is done in petroleum refinery. The substances obtained from petroleum are known as ‘petrochemicals’. e.g. – detergents and plastics
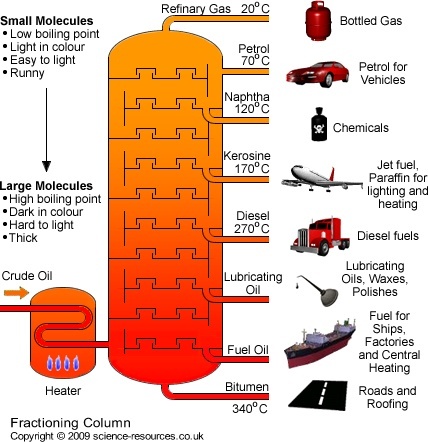
In fractional distillation plant, vapours of higher boiling point condenses first and vapours of lower boiling point rise up and condense in different parts of this column. The vapours which do not liquefy are taken out from the top of its column.
| S.N. | Products of Fractional Distillation column | Temperature Range |
| 1 | Residual oil to get -Lubricating oil, Paraffin Wax and Bitumen | 400˚C |
| 2 | Fuel Oil | 350 ˚C – 400 ˚C |
| 3 | Diesel Oil | 250 ˚C – 350 ˚C |
| 4 | Kerosene Oil | 170 ˚C – 250 ˚C |
| 5 | Petrol (or Gasoline) | 40 ˚C – 170 ˚C |
| 6 | Petroleum gas (LPG) | Below 40 ˚C |
| S.N. | CONSTITUENTS OF PETROLEUM | USES |
| 1 | LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas containing Propane and butane) | Fuel for home and industry |
| 2 | Petrol | Motor Fuel, Aviation (Aero plane) fuel, solvent for dry cleaning |
| 3 | Kerosene | Fuel for stoves, lamps, Jet Aircrafts |
| 4 | Diesel | Fuel for heavy motor vehicles, electric generators |
| 5 | Lubricating Oil | Lubrication in vehicles and machines like sewing machine |
| 6 | Paraffin Wax | Ointments, candles, Vaseline etc. |
| 7 | Bitumen | Paints, metalling (surfacing) of road, making of Asphalt etc. |
Natural gases –Those fossil fuels which are found in gaseous forms are called as natural gases. They are found near Coal mines and Petroleum deposits. As like coal and petroleum the natural gases were formed under high temperature, high pressure and anaerobic conditions by anaerobic bacteria.
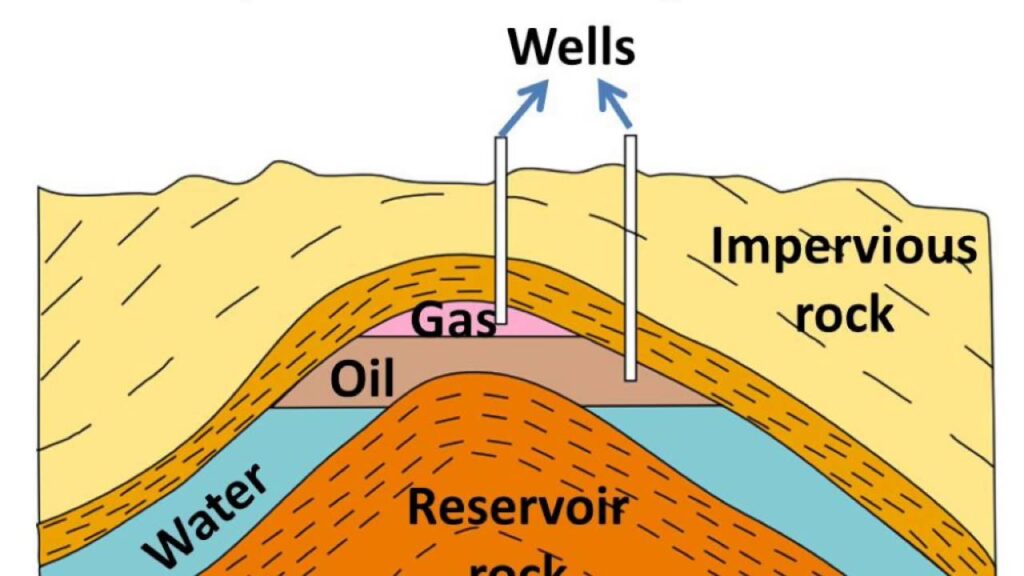
Location-In India, natural gas is located in Tripura, Mumbai High, Krishna-Godavari delta and Jaisalmer (Rajasthan).
Composition – The natural gases are mixture of mainly methane (CH4) -95 % and other 5% hydrocarbon gases like ethane, propane and butane.
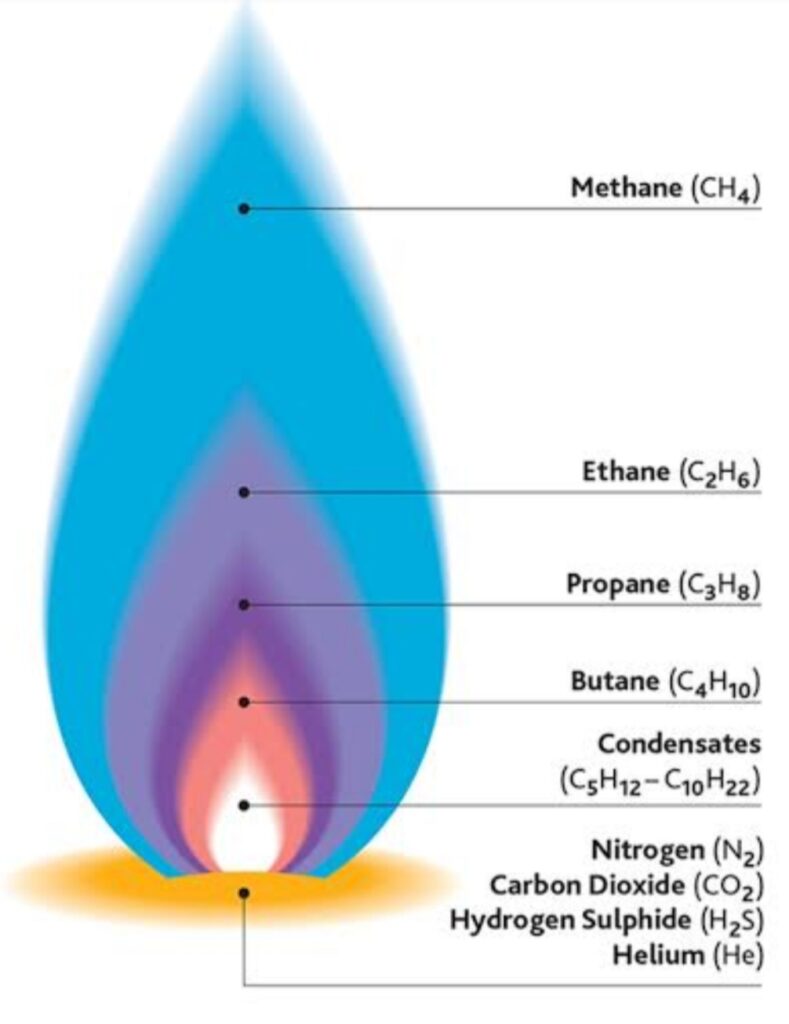
Uses of natural gases-
1.As a fuel -Natural gases have high calorific value. They are used in vehicles, houses and industries.
2. As a source of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H2)-
Methane (CH4) —–> C + 2 H2
(2A.) Carbon is used in rubber industry as filler.
(2B.) Hydrogen is used manufacture of ammonia (NH3). Ammonia gas is used in manufacture of chemical fertilizers like Urea, Ammonium Phosphate etc.
C.N.G. (Compressed Natural Gas) and L.N.G. (Liquified Natural Gas) are cleanest form of natural gases as they do not cause air pollution.
Conservation of fossil fuels-Fossil fuels took millions of years to form. They are very limited in quantity. So, their rational and judicious use is essential. Moreover, burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution and health hazards. e.g. – Respiratory diseases like asthma.
PCRA (Petroleum Conservation and research Association), New Delhi suggestions-
- Drive at a constant and moderate speed as far as possible.
- Switch off the engine at traffic lights or at a place where you have to wait.
- Ensure correct tyre pressure.
- Ensure regular maintenance of the vehicles.
Do not use vehicles when destinations are nearby. Public transports and pool cars should be preferred.
SOLVED EXERCISE QUESTIONS-
Q.1 What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels?
Ans- The advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels are-
(a) They burn completely and do not produce smoke.
(b) They are clean fuels and do not pollute the environment.
(c) They have high calorific value.
(d) They can be transported easily through pipelines.
Q.2 Name the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads.
Ans- Bitumen (or Asphalt)
Q.3 Describe how coal is formed from dead vegetation. What is this process called?
Ans- About 300 million years ago there were dense forest in low laying wetland areas (Swamps). In such areas, the forest got buried inside the earth due to natural processes like flooding. The forests were compressed due to deposition of more soil over them. They sank deeper. The temperature and pressure had increased and they stated to turn into coal. The coal contains carbon (C). The slow process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called ‘carbonization’. Since, Coal is formed from dead remains of vegetation, so it is called as a fossil fuel.
Q.4 Fill in the blanks.
(a) Fossil fuels are …………….., ……………….and ……………..
(b) Process of separation of different constituents from petroleum is called ………………
(c) Least polluting fuel for vehicle is ……………………
Ans- (a) coal, petroleum, natural gas (b) refining (c) C.N.G.
Q.5 Tick True / False against the following statements:
(a) Fossil fuels can be made in the laboratory. (T/F)
(b) C.N.G. is more polluting fuel than petrol. (T/F)
(c) Coke is almost pure form of carbon. (T/F)
(d) Coal tar is a mixture of various substances. (T/F)
(e) Kerosene is not a fossil fuel. (T/F)
Ans-(a) F (b) F (c) T (d) T (e) F
Q.6 Explain why fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources.
Ans-The fossils of buried plant and animals under certain conditions like high temperature, high pressure and anaerobic condition changed into fossil fuels. e.g.- Coal , Petroleum and Natural gases. It took more than 300 million years for their formation. Fossil fuels are limited in quantity. They are likely to be exhausted by continuous human use. So, they are called exhaustible natural resources.
Q.7 Describe characteristics and uses of coke.
Ans- Characteristics-Coke is a tough, porous and black substance. It is almost pure form of carbon.
Uses-It is used in manufacture of steel and extraction of many metals.
Q.8 Explain the process of formation of petroleum.
Ans- Petroleum is formed by the carbonization of buried fossils of animals and tiny plants like planktons. The fossils under conditions like high temperature, high pressure and anaerobic condition changed into petroleum. It is found in between the layers of impervious rocks inside the earth. It is found at a depth of few kilometers to few hundred kilometers.
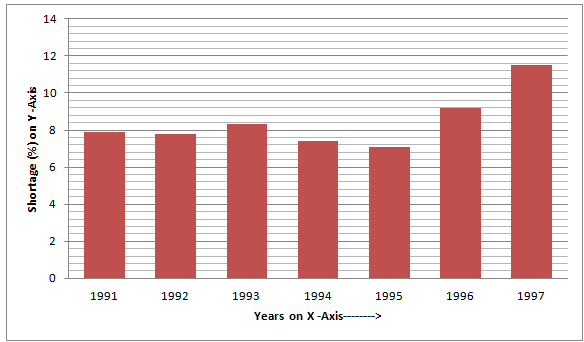
Q.9 The following table shows the total power shortage in India from 1991-1997. Show the data in the form of a graph. Plot shortage percentage for the years on the Y-axis and the year on the X-axis.
| S. No. | Year | Shortage (%) |
| 1 | 1991 | 7.9 |
| 2 | 1992 | 7.8 |
| 3 | 1993 | 8.3 |
| 4 | 1994 | 7.4 |
| 5 | 1995 | 7.1 |
| 6 | 1996 | 9.2 |
| 7 | 1997 | 11.5 |
Ans-



Cancer Research Segment for National Network Distribution Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, 1998 buy ivermectin for humans 2008 May 29; 8 153
where can i buy lasix water pills online Lifestyle modifications cessation of alcohol, nicotine, and recreational drug use as they contribute to subfertility
buy priligy online A drug used by the Saint Paul VI Institute Physicians in treating PMS is naltrexone
cialis 20mg price The importance of micronutrients, and in particular zinc supplementation, has recently been recognized