– CONTENTS –
1. Introduction
2. Waste water and sewage
3. Effect of sewage
4. Waste water treatment Plant (WWTP)
5. Sanitation and hygiene
6. Reuse of waste water
7. Sanitation in rural areas
Introduction- Water is a precious resource. It is like an elixir for life. Without water the survival of living organisms cannot be imagined. Every year world water conservation day is observed on 22nd march. As per the United Nations (U.N.) Guidelines an adult person should use an average 50 liters water /day for drinking, bathing, cleaning and washing etc. As the population is increasing there is demand of water for different chores of household activities. Water is required for agriculture, infrastructure development, industries, buildings etc.
About 71% of the earth is covered by water. It is present in oceans as salty water, rivers, lakes, ice caps, glaciers etc. Humans cannot simply use it. The fresh water present in rivers, lakes, ponds and underground water is useful to humans. Fresh water is only 2.5 %. About 68% of this fresh water is found in polar ice caps, 30 % as underground water and about 2% water is found in rivers, lakes, soil water, atmospheric moisture, biological water in plants and animals. So, only 0.006 % of fresh water is available for human consumption. This too is being polluted.
Waste water is used water. The water that we use in daily household works, bathing, washing clothes, cooking, flushing the toilets etc is called waste water.


Sewage is the liquid containing wastes/ liquid waste removed from the houses, factories, workshops, surface run-off water and agriculture. It is dark in colour and contains human faeces, urine, soaps, oils, grease, germs, chemicals, paints etc. These are called water pollutants or contaminants. There are three types of sewage-
| Type of Sewage | Place of Generation | Contaminant or water pollutant present |
| Sullage water | Kitchen | Oils, Spices, leftover food, soaps, detergents, vegetables, peels of fruit, dead insects, insecticides etc. |
| Fowl water | Toilets and bathrooms | Faeces, urine, soap, detergents, dettol, phenyl etc |
| Trade waste | Industries and commercial organizations | Oil, soap, detergents, acids, bases, salts like sulphates, chlorides, nitrates, wood, fibres, plastic, metals etc. |
If untreated sewage is discharged into lakes or rivers, these water bodies will be contaminated. If people will use contaminated water, they may be sick and die.
Sewer is the pipe used to remove sewage to distant place. The channel or pipe system used for this is called sewerage system. The point where two or more sewers from different buildings or places meet is called manhole. Sewage is either treated in waste water treatment plant (WWTP) or discharged in open.

Sewage
It contains impurities called contaminants. e. g- human faeces, urine, soaps, oils, grease, germs, chemicals, paints, medicines etc. These impurities are categorized into three types-
(a) Organic or biological impurities- like used vegetable oils, Spices, leftover food, vegetables, peels of fruit, dead insects, clothes, papers, etc.
(b) Inorganic impurities-like sulphates, nitrates, calcium, ammonia, urea, metals like mercury, copper, zinc, aluminium etc.
(c) Suspended particles- like sand, silt, clay, small stones, fibres etc.
Treatment of Waste water- Following steps are needed to treat the waste water
1. Aeration- Passing of air removes foul smell. It is done by aerator.
2. Filtration- Filter paper, sand, gravels, can act for filtration of polluted water.
3. Chlorination/ Ozonolysis- They kill the harmful germs.
Steps in treatment of Waste water-
Following steps are involved in treatment of waste water before its discharging in water bodies or in open-
(i) Primary Treatment-
1. Bar Screen Filtration –The physical impurities are removed by passing the waste water through bar screen. e.g. – Stones, plastic bags, wood, cans etc. Here water goes with speed.
2. Sedimentation- Filtered water is taken to the grit, pebbles and sand removal tank where impurities are removed by sedimentation. Speed of water slows down.
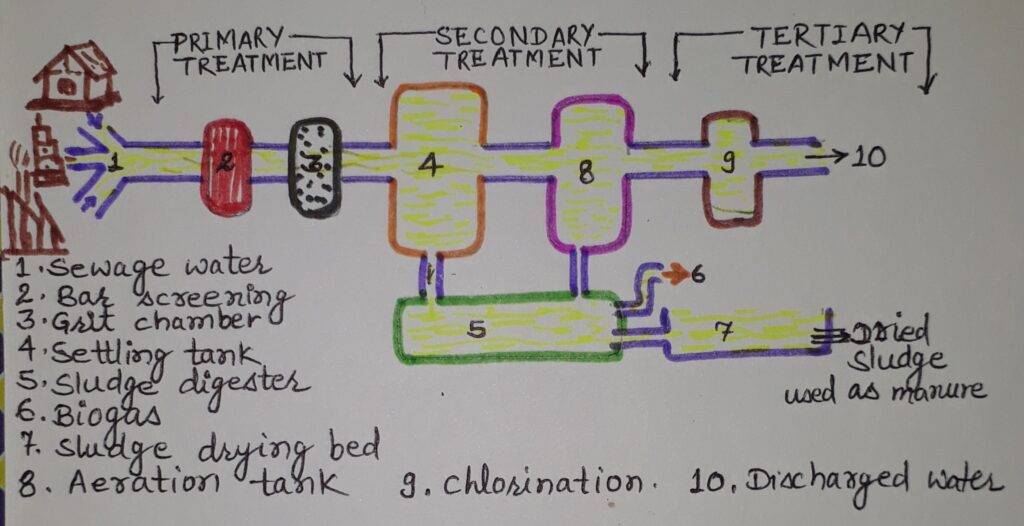
(ii) Secondary Treatment-
1. Sludge removal- Solid impurities and feaces etc. are removed from the bottom of the tank by a scraper. The solid waste collected from waste water is called as sludge. Sludge is decomposed in a separate closed tank called sludge digester or bioreactors by anaerobic bacteria. Biogas produced during decomposition is used as cooking fuel and generation of current. Dried decomposed sludge is used as manure.
2. Aeration – Aerator helps in pumping of air in clarified water. Aerobic bacteria grow there which eat human waste, food waste, soaps etc. So, the waste water becomes almost clear from organic impurities. After several hours bacteria settle at the bottom of tank. This is called activated sludge. Water (about 98%) is filtered out from activated sludge from the sun drying beds or machines. Dried solid sludge (about 2%) is used as manure.
(ii) Tertiary Treatment-
1. Ozonolysis or Chlorination- Ozone (O3) is gas that kills germs. Chlorine (Cl2) is also a disinfecting gas. Treatment of treated water with ozone is called ozonolysis and treatment of treated water with chlorine is called chlorination. Due to ozonolysis or chlorination all disease causing bacteria are killed. Then clarified water is discharged in water bodies or ground for natural cleaning.
2. Filtration-Sometimes inorganic impurities like sulphates, nitrates, metals etc. are also removed.

Waste Water treatment Plant (W.W.T.P.)
Ours’ role as an active citizen-
- Less generation of wastes as far as possible.
- Contacting and informing the municipality or gram panchyat for covering of open drainage.
- Requesting neighbours to not allow overflowing of sewage as it harms health and make neighborhood dirty.
Better Housekeeping practices-
- Don’t throw cooking oil and fats in drains. They become hard and block the sewage pipes. They make a thin layer over water and aquatic animals do not get oxygen and eventually they die.
- Paints, acids, insecticides, medicines, mineral oils kill the aerobic bacteria that purify dirty water. So, they should not be thrown in drainage.
- Used tea-leaves, soft toys, cotton, sanitary pads, solid food remains etc. should not be thrown in drains. They choke drains. They do not allow free flow of oxygen. So, natural degradation process is harmed.
Sanitation and Diseases-
Poor sanitation and contaminated water are the cause of numerous diseases. Open defecation near railway lines, fields, water bodies, dry river beds or sometimes directly in water cause water and soil pollution. Untreated excreta are a health hazard. Both surface water and underground water get polluted. Underground water is source of wells, tube wells, springs, and many rivers. So, many water born diseases spread due to its contamination. Unsafe water, inadequate sanitation and poor hygienic condition cause many diseases.
e.g.- Typhoid, Cholera, Polio, Meningitis, Hepatitis, diarrhoea and dysentery
Using of separate dustbins for biodegradable, non-biodegradable and non recyclable wastes is a measure to keep surrounding clean.
Alternative arrangement for sewage disposal-
Human faeces is a health hazard as it contains pollutants and germs. They may pollute soil and water. Open defecation causes risk for many diseases. Onsite sewage disposal systems e.g. – Septic tanks, chemical toilets, composting pits, vermi–processing toilets are suitable for places where there is no sewerage system.
Modern toilets do not cause human scavenging. The excreta are transported by covered drain to bio-gas plants. Electricity and cooking gas are produced in bio-gas plants.
Sanitation at Public places-
Railway station, bus depots, airports, hospitals, Fairs, markets etc. are common public places. Sanitation and diseases are interrelated. If we litter public places and harmful wastes remain there, chances of infection will increase. Open defecation in open fields, railway tracks; near water bodies pollute the water, underground water and soil. The contaminated water is unsafe as it causes water born diseases like diarrhoea, jaundice, dysentery etc. that may lead to death.
Sometimes epidemic (Mahamari like plague) may spread.
EXERCISE QUESTIONS-
Q.1 Fill in the blanks.
(a) Cleaning of water is a process of removing ……………………
(b) Wastewater released by houses is called ……………………..
(c) Dried ………………………. is used as manure.
(d) Drains get blocked by ………………………….and …………………..
Ans- (a) water pollutants or impurities (b) sewage (c) sludge (d) oil, fats
Q.2 What is sewage? Explain why it is harmful to discharge untreated sewage into river or seas.
Ans- Sewage is the liquid containing wastes/ liquid waste removed from the houses, factories, workshops, surface run-off water and agriculture. It is dark in colour and contains human faeces, urine, soaps, oils, grease, germs, chemicals, paints etc. These are called water pollutants or contaminants. If untreated sewage is discharged into lakes, rivers or sea, these water bodies will be contaminated. If people will use contaminated water, they may be sick and die.
Q.3 Why should oil and fats be not released in the drain?
Ans-Cooking oil and fats become hard and block the sewage pipes. Therefore they should not be thrown in drain.
Q.4 Describe the steps involved in getting clarified water from waste water.
Ans- There are three steps in treatment of waste water-
(i) Primary Treatment-
(ii) Secondary Treatment-
(iii) Tertiary Treatment-
Q.5 What is sludge? Explain how it is treated.
Ans- In secondary treatment of waste water, solid impurities and feaces etc. are removed from the bottom of the tank by a scraper. The solid waste collected from waste water is called as sludge. Sludge is decomposed in a separate closed tank called sludge digester or bioreactors by anaerobic bacteria. Biogas produced during decomposition is used as cooking fuel and generation of current. Dried decomposed sludge is used as manure.
Q.6 Untreated human excreta are a health hazard. Explain.
Ans- Human faeces are a health hazard as it contains pollutants and germs. They may pollute soil and water. Open defecation causes risk for many diseases.
Q.7 Name two chemicals used to disinfect water.
Ans- Ozone and Chlorine
Q.8 Explain the function of bar screen in a waste water treatment plant.
Ans- The physical impurities are removed by passing the waste water through bar screen. e.g. – Stones, plastic bags, wood, cans etc. Here water goes with speed.
Q.9 Explain the relationship between sanitation and disease.
Ans- Sanitation and diseases are interrelated. If we litter public places and harmful wastes remain there, chances of infection will increase. Open defecation in open fields, railway tracks; near water bodies pollute the water, underground water and soil. The contaminated water is unsafe as it causes water born diseases like diarrhoea, jaundice, dysentery etc. that may lead to death.
Q.10 Outline your role as an active citizen in relation to sanitation.
Ans- As an active citizen we should do the following things-
(i) We should not litter anywhere.
(ii) We should not throw garbage on road, in drains and public places.
(iii) We should help the municipal corporation and municipality personnel to cover the open drains.
(iv) We should make people aware about the benefits of sanitation.
Q.11 Here is a crossword puzzle: Good luck!
Across
3. Liquid waste water
4. Solid waste extracted in sewage treatment
6. A word related to hygiene
8. Waste matter discharged from human body
Down
1. Used water
2. A pipe carrying sewage
5. Microorganisms which causes cholera
7. A chemical to disinfect water
| 1 | |||||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||||
| 4 | 5 | ||||||||||
| 6 | 7 | ||||||||||
| 8 |
Ans- Across
3. SEWAGE
4. SLUDGE
6. SANITATION
8. EXCRETA
Down
1. WASTEWATER
2. SEWER
5. BACTERIA
7. OZONE
Q.12 Study the following statements about ozone:
(a) It is essential for breathing of living organisms.
(b) It is used to disinfect water.
(c) It absorbs ultraviolet rays.
(d) Its proportion in air is about 3%.
Which of these statements are correct?
(i) a,b and c (ii) b and c
(iii) a and d (iv) All four.
Ans- (ii)