Introduction – Light is a form of energy that gives a sense of vision. Light helps in viewing any object when in returns back from that (reflection of light) to our eyes. We see the objects when the light lights up them. The study of light and its phenomenon is called ‘optics’.
e.g.- We see the pen because the light falling on the pen is reflected back to our eyes.
e.g.- When light enters from a ventilator of a dark room, we see the dust particles of air.
Sources of light- Anything that produces light is called as source of light. They are also called as luminous objects. There are two types of sources of light- Natural and Artificial.
(a) Natural Sources e.g.- The Stars, The Sun, Fireflies etc
(b) Artificial/ Man-made Sources e.g.- Burning Lamp, Candle, Bulb, L. E. Ds, etc.
The objects on which light falls from any luminous object and we can see the after reflection are called illuminated objects. e. g.- Moon, Table etc.
How light travels- Light travels in a straight pathway. The Straight pathway along which the light travels is called ‘Ray of Light’. The rays of light are always parallel to each other. A group of light rays is called as ‘Beam or Pencil of Light’. In a beam, the light rays may be parallel, converging or diverging to each other.
Speed of Light in air=3 x 108 m/s= 300000 km/s= 3 x 10 10 cm/s
Reflection of Light- The change in the direction of light due to any reflective surface is called as ‘reflection of light’. The plane mirror, shiny polished surfaces, shiny metal surfaces act as reflective surfaces. They also form image of an object.

Reflection of Light © www.vkscience.com
When light pass through the lens or any transparent or translucent medium, there occurs ‘refraction of light’.
Plane Mirror- The light rays coming from any object get reflected from the plane mirror form the image in the mirror. Following are the characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror-
(i) The image is upright.
(ii) The size of image is equal to the size of object.
(iii) The image is formed behind the mirror i.e. the image is virtual.
(iv) The distance of image from the mirror is equal to the distance of object from the mirror.
(v) The image cannot be touched.
(vii) The image cannot be obtained on the screen.
(vii) The image is laterally inverted i.e. left part of image is right part of object and vice versa.
Spherical mirrors- The mirror which is a part of large spherical piece of glass and one side of which is silvered is called a spherical mirror. There are two types of spherical mirrors-
(a) Concave mirror- Its reflective part is curved inside. It converges the incoming light at the focus. It is also called a converging mirror.
(b) Convex mirror- Its reflective part is curved outward. It diverges the incoming light. It is also called as diverging mirror.
Nature of image formed by a concave mirror –When object is placed very close to the concave mirror, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified. Concave mirror can also form real and inverted image of an object.
Nature of image formed by a convex mirror- The convex mirror always forms erect, virtual and smaller images than the object.
Applications of Concave and Convex mirrors-
1. Concave mirror is used by dentist and E.N.T. Specialists to examine their patients.
2. Concave reflective surface is used in the head lights of vehicles and torch.
3. Convex mirror has large field view. So, it is used as side mirror in vehicles.
4 Convex mirrors are used as corner mirrors.
Lens- A lens is a combination of two refractive pieces of glass.
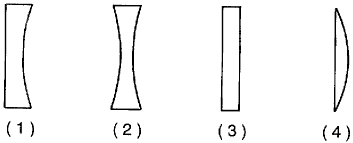
There are four types of lens-
1. Concave lens
2. Convex Lens
3. Plano-concave lens
4. Plano-convex lens
Images formed by lenses-
1. Concave lens -This lens is thinner at the center than the edge i.e. curve inward. It always forms erect, virtual and smaller image than object. It is also called as diverging lens.
2. Convex lens- This lens is thicker at the center than the edge curved outward. It forms real and inverted image. But, when object is very close it forms virtual, erect and magnified image. It is also called as converging lens.
Uses of Lenses-
1. Concave lens is used to correct myopia or short-sightedness.

Concave Lens © www.vkscience.com
2. Convex lens is used to correct the hypermetropia or long nearsightedness or shortsightedness. It is also used a magnifying glass.

Convex Lens © www.vkscience.com
Converging and Diverging Rays of Light- Those reflected or refracted rays which meet at any point are called converging rays. The concave mirror and convex lens converges the incoming light rays at the principal focus.
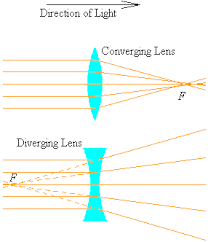
Source: Hugohouse.org
Those reflected or refracted rays which do not meet at any point are called as diverging rays. The convex mirror and concave lens diverges the incoming light rays.
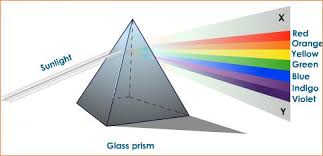
Nature of Sunlight- The sunlight or white light consist of seven colours. When the white light is passed through a glass prism, we get seven different colour spectrum on the screen. This phenomenon is called dispersion of light. When sunlight falls on a Compact Disc (CD) then many colours can be seen. The soap bubbles also show many colours when sunlight falls on them.
Newton’s Disc- Isaac Newton performed an activity in which a circular disc was divided into 7 equal parts. Wit was attached with a central disc. When disc was rotated very fast then all the seven colours merge and appear as white colour.
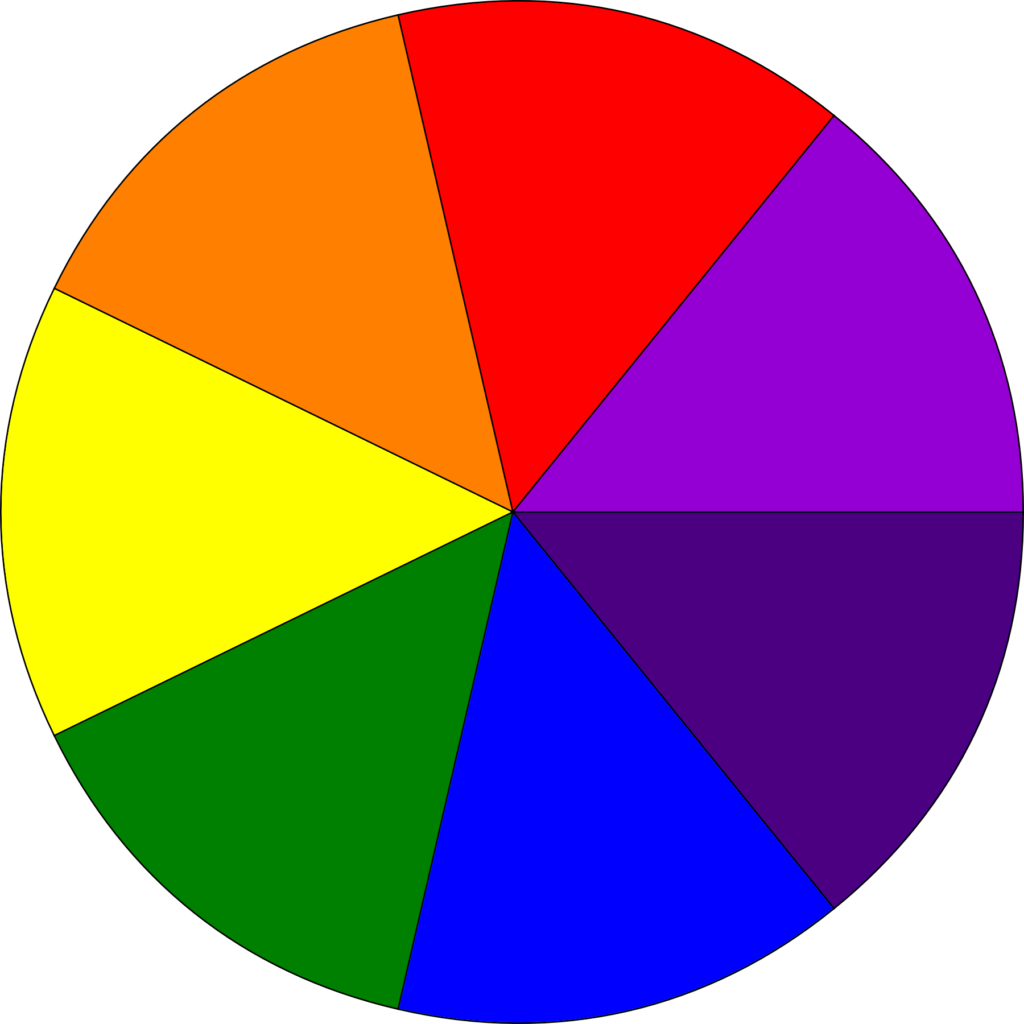
Newton’s Disc
Fig. Newton’s Disc
EXERCISE QUESTIONS-
Q.1 Fill in the blanks:
(a) An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called ……………………
(b) Image formed by a convex ……………….is always virtual and smaller in size.
(c) An image formed by a ………….mirror is always of the same size as that of the objects.
(d) An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a ………..image.
(e) An image formed by a concave …………….cannot be obtained on a screen.
Ans- (a) virtual image (b) mirror (c) plane (d) real (e) lens
Q.2 Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(a) We can obtain an enlarged and erect image by a convex mirror.
(b) A concave lens always forms a virtual image.
(c) We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror.
(d) A real image cannot be obtained on a screen.
(e) A concave mirror always forms a real image.
Ans- (a) F (b)T (c) T (d) F (e) F
Q.3 Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of column II.
Column I Column II
(a) A plane mirror (i) Used as a magnifying glass
(b) A convex mirror (ii) Can form image of objects spread over a large area.
(c) A convex lens (iii) Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth.
(d) A concave mirror (iv) The image is always inverted and magnified.
(e) A concave lens (v) The image is erect and of same size as the object.
(vi) The image is erect and smaller than the object.
Ans- (a) –v (b) –ii and iv (c)-I (d)-iii (e)- vi
Q.4 State the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Ans- Following are the characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror-
(i) The image is upright.
(ii) The size of image is equal to the size of object.
(iii) The image is formed behind the mirror i.e. the image is virtual.
(iv) The distance of image from the mirror is equal to the distance of object from the mirror.
(v) The image cannot be touched.
(vii) The image cannot be obtained on the screen.
(vii) The image is laterally inverted i.e. left part of image is right part of object and vice versa.
Q.5 Find out the letters of English alphabet or any other language known to you in whom the image formed in a plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself. Discuss your findings.
Ans- A,H, I, M,O,T, U,V, W, X and Y in English alphabet.
Q.6 What is a virtual image? Give one situation where a virtual image is formed.
Ans- An image that cannot be obtained on the screen is called as virtual image. The image formed by plane mirrors is virtual images. The image is virtual when an object is placed close to the convex lens.
Q.7 State two differences between a convex and a concave lens.
Ans-
| S.N. | CONCAVE LENS | CONVEX LENS |
| 1 | This lens is thinner at the center than the edge i.e. curve inward | This lens is thicker at the center than the edge curved outward. |
| 2 | It always forms erect, virtual and smaller image than object. | It forms real and inverted image. But, when object is very close it forms virtual, erect and magnified image. |
Q.8 Give one use each of a concave and a convex mirror.
Ans- Concave Mirror- Head light of motor vehicles.
Convex Mirror- Rear view Mirror in Vehicle.
Q.9 Which type of mirror can form a real image?
Ans- Concave mirror
Q.10 Which type of lens always forms a virtual image?
Ans- Concave lens
Choose the correct option in questions 11-13
Q.11 A virtual image larger than the object can be produced by a
(i) Concave lens (ii) Concave mirror
(iii) Convex mirror (iv) Plane mirror
Ans- (ii) Concave mirror
Q.12 David is observing his image in a plane mirror. The distance between the mirror and his image is 4 m. If he moves 1 m towards the mirror, then the distance between Davis and his image will be-
(i) 3 m (ii) 5 m
(iii) 6 m (iv) 8 m
Ans- (iii) 6 m
Q.13 The rear view mirror of a car is a plane mirror. A driver is reversing his car at a speed of 2 m/s. The driver sees in his rear view mirror the image of a truck parked behind his car. The speed at which the image of the truck appears to approach the driver will be-
(i) 1 m/s (ii) 2 m/s
(iii) 4 m/s (iv) 8 m/s
Ans- (ii) 2 m/s
© www.vkscience.com




What should I tell my Ro affiliated provider before using bupropion SR cialis for sale