LEARNING OBJECTIVES-
- DISCOVERY OF CELL AND CELL
- THE VARIETY OF CELLS
- THE STRUCTURE OF CELLS
- THE FUNCTIONS OF CELLS
- TYPES OF CELLS
- COMPARISON BETWEEN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
DISCOVERY OF CELL-
The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 in cork cells. He discovered small pit or chamber like structures in cork plug of bottles and called them as ‘cells’. The study of cells is called ‘cytology’.
CELL- The structural and functional unit of organism is called ‘cell’. Cells are similar to the bricks of a wall. The cells form the body of an organism. All the functions of the organisms are performed by the cell. Different group of cells perform different functions. A group of cells that have common origin and function is called ‘tissue’. E.g. -Nervous tissue, Bone tissue, Muscular tissue, Blood tissue etc. The study of tissue is called ‘histology’.
THE VARIETY OF CELLS– The cells show varieties in terms of number, shape and size.
VARIETY IN NUMBER OF CELLS– Some organisms are made up of just one cell; they are called as unicellular organisms. The one cell body does all the functions like respiration, digestion, excretion, growth, reproduction etc. e. g.- Amoeba, Paramecium etc.
Some organisms are made up of more than one cell are called multicellular organisms. The life of organisms having billions of cells begins from one cell called ‘zygote’ (a fertilized egg). The large organisms have more cells. e. g. Plants, Animals etc.
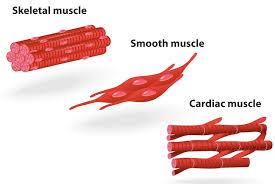
VARIETY IN SHAPE OF CELLS-On the basis of structure and function cells can be of many types. The shape of cells is based on their functions. Cells undergo differentiation to do different functions.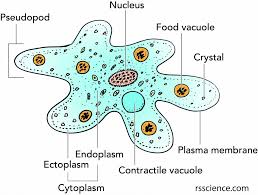
- Discoid shaped e.g.- R.B.Cs
- Spindle shaped e.g.- Muscle cells
- Irregular shaped e.g.- W.B.Cs, Amoeba- Its shape can change.
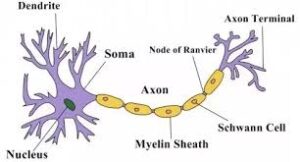
- Long, branched shape. E.g.- Nerve/ Nervous cell
-Longest cell-Neuron (Nerve cell)
-Biggest cell- Ostrich cell
VARIETY IN SIZE OF CELLS- The size of cells is related to their functions. The smallest cell is bacteria. Their size can be as small as 0.1 mm to 0.5 mm (micrometer). The largest cell is ostrich egg. Its size can be 170 mm x 130 mm.
The sizes of cells have no relation with the size of organism. e.g.- the rat and elephant have same size of nerve cells and they perform came functions.
TYPES OF CELLS –
Since the time of Aristotle, the living organisms are broadly categorized into Plants and Animals. On the basis of this there are two broad categories of cells-
A. Plant Cells B. Animal cells
But, in this classification, bacteria and other small organisms don’t fit. So, another classification of cells was propounded. According to this cells are of two types-
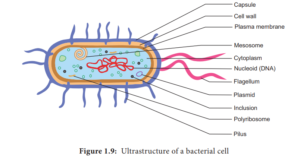
A. Prokaryotic cells like- Bacteria
B. Eukaryotic cells like – Plant cells, Animals cells, Amoeba, Plasmodium, Fungi etc.
THE STRUCTURE OF CELLS-
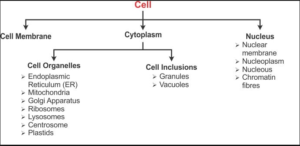
The cell can be conveniently divided into three parts-
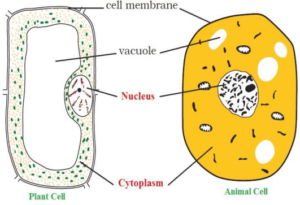
A. Cell membrane
B. Cytoplasm and
C. Nucleus
The shape of plant cells are fixed due to cell wall while the shape of some of the animal cells is irregular.
1.Cell Wall– It is a permeable membrane in the plant cells. It is very tough. It is outside the cell membrane.The shape of plant cells are fixed while the shape of animal cells is irregular due to cell wall. The cell wall is also found in bacterial cells.
2.Cell-membrane – It is the outer protective layer of cells. It is found in plant cells as well as animal cells. It is selectively permeable.
3.Cytoplasm– It is a jelly like substance in between the cell membrane and nucleus. It is the living matter of the cell. In the cytoplasm gases, water , organic matter, enzymes etc. are found.If the cytoplasm and nucleus are present, the cell will be living. In the cytoplasm many types of cell organelles are found. The are – Mitochondria, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, Ribosomes, Lysosome , centrosome, Plastids like Chloroplast , Chromoplast and Leucoplast etc.
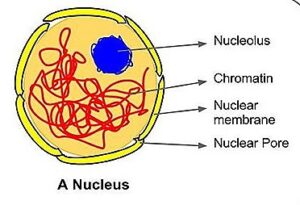
4. Nucleus– It is found in the living matter (Cytoplasm) of the cell. It controls almost all the activities of the cell. It is true or fully developed in eukaryotic cells of plants, animals, amoeba etc.
It has nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, chromosomes and nucleolus. Nucleus is a round dense cell organelle. The threads like structures in the nucleoplasm of nucleus are called as chromosomes. Chromosomes are basically made up of D.N.A. (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and histone protein.
In prokaryotic cells of bacteria and Cynobacteria (blue-green algae) there is an incipient or primary nucleus or nucleoid. It is not organized and fully developed as like eukaryotic cells. It is represented by D.N.A. only.
Genes are the functional unit of Chromosomes. The genes help in inheritance of characters i.e. transfer of characters from one generation to next. They determine the characteristics of organisms.
5. Plastids – They are found in plant cells and certain bacteria and protozoa like Euglena. Plastids are of three types-
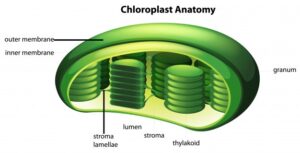
A. Chloroplasts- They contain chlorophylls and help in photosynthesis by entrapping sunlight. They are green plastids.
B. Chromoplast- They are of different colours other than green. Chromoplasts impart colours to flowers, fruits and leaves.
C. Leucoplasts- They are colourless plastids. They store the food prepared by plants. It is found in roots.
All the three types of plastids can be seen in potato tubers. Schimper discovered plastids.
6. Vacuoles – They are empty structures in the cytoplasm. Vacuoles contain some liquids and provide stability to the shape of cells. They are large size in plant cells and very small in animal cells or absent.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANT CELLS AND ANIMAL CELLS-
|
S.N. |
PLANT CELL |
ANIMAL CELL |
|
1 |
They have cell wall |
Cell wall is absent. |
|
2 |
They have chloroplast. |
Chloroplast is absent. |
|
3 |
They have large vacuole |
Vacuole is very small or absent. |
|
4 |
Lysosome present |
Lysosome absent. |
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANT CELLS AND ANIMAL CELLS –
|
S.N. |
PLANT CELL |
ANIMAL CELL |
|
1. |
Cell wall present. |
Cell wall absent. |
|
2. |
Chlorophylls present. |
Chlorophylls absent. |
|
3. |
Large vacuole present. |
Vacuole either very small or absent. |
|
4. |
Lysosome absent. |
Lysosome (suicide bags) present. |
EXERCISE QUESTIONS-
Q.1
Answer-
Q.2
Answer-
Q.3
Answer-



This comment has been removed by the author.