CONTENTS-
1. Importance of water
2. Sources of water
3. Water cycle
4. Terminology pertaining to water (Hydrological) cycle
5. Flood
6. Drought
7. Conservation of water
8. Rainwater harvesting
9. Potable water
1. Importance of water- Water is a precious resource. It is like an elixir for life. Without water the survival of living organisms cannot be imagined. Water is found in solid, liquid and gaseous states. About 97 % water of surface water is found in oceans and sea as salty water. About 3 % of surface water is present as fresh surface water. But, that too is not accessible. We have only 1 % water available for human consumption. So, the judicious use of water is imperative. Following are the common uses of water-
1. Water is used by all plants and animals for their basic life processes.
2. Water make aquatic habitat for aquatic plants and animals.
3. Water is used for house hold works like bathing, washing, cooking etc.
4. It is used in agriculture for irrigation of crops.
5. Dam water is used for generating the hydroelectricity at hydroelectric power stations.
6. Water is used in many industries.
7. Water transportation is used to carry passengers and good. Its cost is comparatively lowest.
8. Water puts off fire.
9. Water helps in regulating the climate of the area due to evaporation.
Activity- To estimate daily water requirement by you and your family.
Theory– Water is required for different household chores. . As per the, United Nations (U.N.) Guidelines an adult person should use an average 50 liters water /day for drinking, bathing, cleaning and washing etc.
Requirements- Buckets, mugs etc. to estimate the water to be used. An approximate estimate can also be taken under teacher’s or parent’s guidance.
Methodology- Fill the amount of water used in different activities.
| S.N. | ACTIVITIES | AMOUNT OF WATER USED (in Liters) |
| 1 | Drinking | ………………… |
| 2 | Brushing | ………………… |
| 3 | Bathing | ………………… |
| 4 | Toilets | …………………. |
| 5 | Washing clothes | …………………. |
| 6 | Washing utensils | ………………….. |
| 7 | Floor cleaning | …………………… |
| 8 | Supplying water to garden plants or any other activity | …………………….. |
| Total amount of water used per day by a family= | …………………… liters |
2. Sources of water-
The sources of water can be categorized into surface water sources and underground water sources. The water present in oceans, rivers, lakes, ponds, streams, glaciers, ice caps etc. is called surface water. The surface water is less in percentage than the underground water. The ground water is obtained from wells, hand pumps, tube wells and springs. The level of ground water below which only water is found, is called water table. Water table goes down in summer season or due to excess taking of underground water. Underground water is found above non-pervious bedrock.
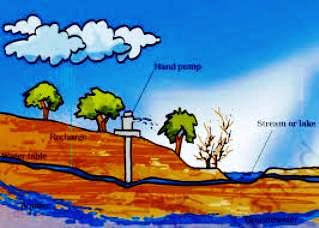
Underground Water
3. Water cycle– The cyclic rotation of water from the surface of the earth to the atmosphere and back to the earth is called water cycle. The plants release water vapour from their leaves through a process called transpiration. The water from ocean, river, lakes like water bodies, wet clothes, cooking etc. change to water vapour due to heat by evaporation process. The respiration by animals also releases the water vapours. The warm water vapours rise up in the atmosphere and become cool. At a sufficient height, the water vapours condense and change into tiny water droplets. So many tiny droplets come together to form the clouds. The clouds contain water. When clouds collide with each other, rainfall occurs and water returns back to the earth.
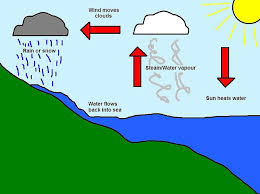
Water Cycle (Source: Google Image)
4. Terminology pertaining to Water (Hydrological) cycle-
1. Transpiration– The loss of water from leaves of plants in form of water vapour is called transpiration.The rate of transpiration increases in daytime and in summer season.
2. Evaporation / Vaporization- The process of changing of liquid water into water vapour is called evaporation or vaporization. Evaporation occurs at all temperatures. When temperature is high, rate of evaporation increases. In evaporation, water vapours are formed.
3. Respiration-We release water vapour also with other gases during exhalation.
4. Cooking and boiling of water- In both processes water vapours are formed.
5. Condensation- The water vapour is a gas. It goes up in the upper layers of atmosphere. Above the atmosphere, the temperature lowers down. So, the water vapours change into liquid and then solid water in clouds. It is called condensation.
6. Precipitation/Rainfall– Due to rainfall the water returns back to the earth.
5. Flood-
When rainfall occurs for several days, it results into flood. The water bodies like ponds, lakes, rivers are filled up and the water flows over to submerge the road, houses, agricultural fields etc. Flood fury is a worldwide phenomenon. It occurs particularly in Asia causing deaths of people. Bangladesh China and India are most affected countries due to flood.

Photo . 1 Flood (Source: Google Image)

Photo. 2 Flood (Source: Google Image)
Causes of Flood-
- High and Continuous rainfall for several days.
- Cloud bursting .e.g. – Badrinath, Uttarakhand incident.
- Cyclonic rainfall
- Breaking of dams, river banks, canals and reservoirs
- Deposition of sediments in rivers and bed of streams
- Deforestation and shifting (Jhoom) cultivation
Impacts of Flood-
- It causes loss of human and animal lives.
- It causes the submerging of crops and carrying away of soil of croplands.
- It spread of epidemic diseases like cholera, diarrhoea, skin diseases etc.
6. Drought-
The absence of rainfall or scanty rainfall for a long time, results into a drought. Drought results in shortage of food due to lack of production. There will be lack of water and fodder causing loss of livestocks. The terrestrial and aquatic habitats are severely affected. The migration of people and animals stars causing more stress on that area.
The adverse climatic factors are the main cause of drought. But, human activities are also contributing in initiating drought.
7. Conservation of water-Water is in plenty but the water available for human use is only 1 %. This too is being used for industrial purposes, agricultural purposes and infrastructure development. The pollution of fresh water and underground water are cause of concern for their judicious use. What we can do to conserve water are-
(a) Repair leakage taps. (b) Avoid wastage of water. (c) Reduce water pollution. (d) Plant more trees for good climate and role of plants in water cycle (e) The water obtained from sewage treatment can be used in irrigation of crops. (d) Less water consuming crops should be preferred. (f) Industrial waste water should be reused after treatment. (g) Rainwater harvesting is best method for conservation of water.(h) Turn off the running tap while brushing (i) Mopping should be preferred over cleaning the floor
8. Rainwater harvesting- The rainwater is collected to store the water for further use. There are two basic techniques for rainwater harvesting-
(a) Rooftop harvesting- Here rain water is collected from roof.
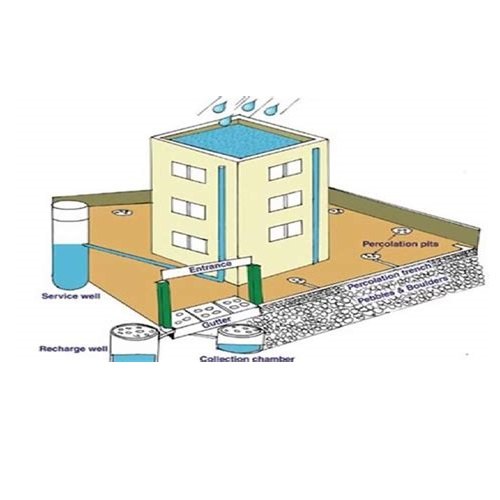
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
(b) Runoff rainwater harvesting- The roadside water is collected in drains to recharge the underground water.
9. Potable water– The water which is fit for drinking is called potable water or drinking water. The removal of physical, chemical and biological impurities from muddy and contaminated water by different methods is called water purification. The solid impurities like soil, sand, salts, urea, metals, germs etc are removed in purification of water.
Exercise Questions-
Q.1 Fill up the blanks in the following:
(a) The process of changing of water into its vapour is called …………….
(b) The process of changing of water vapour into water is called ……………….
(c) No rainfall for a year or more may lead to ……………….in that region.
(d) Excessive rains may cause ……………………
Ans- (a) evaporation (b) condensation (c) drought (d) flood
Q.2 State for each of the following whether it is due to evaporation or condensation:
(a) Water drops appear on the outer surface of a glass containing cold water.
(b) Steam rising from wet clothes while they are ironed.
(c) Fog appearing on a cold winter morning.
(d) Blackboard dries up after wiping it.
(e) Steam rising from a hot girdle when water is sprinkled on it.
Ans- (a) Condensation (b) Evaporation (c) Condensation (d) Evaporation (e) Evaporation
Q.3 Which of the following statements are true “true”?
(a) Water vapour is present in air only during the monsoon. ( )
(b) Water evaporates into air from oceans, rivers and lakes but not from the soil. ( )
(c) The process of water changing into its vapour is called evaporation. ( )
(d) The evaporation of water takes place only in sunlight. ( )
(e) Water vapour condenses to form tiny droplets of water in the upper layers of air where it is cooler. ( )
Ans- (i) False (ii) False (c) True (d) False (e) True
Q.4 Suppose you want to dry your school uniform quickly. Would spreading it near an anghithi or heater help? If yes, how?
Ans- Yes, spreading of wet school uniform near anghithi or heater will evaporate the water due to heat. As a result the uniform will dry quickly.
Q.5 Take out a cooled bottle of water from refrigerator and keep it on a table. After sometime you notice a puddle of water around it. Why?
Ans- When a cooled bottle of water is taken out from refrigerator, water vapours present in air start to condense into puddles of water that can be seen on the bottle.
Q.6 To clean their spectacles, people often breathe out on glasses to make them wet. Explain why the glasses become wet.
Ans- The breath out air contains water vapour. When water vapours collide with the cool surface of the glasses, it condenses and gets attached to glass surfaces. Therefore, the glasses become wet.
Q.7 How are clouds formed?
Ans- The water vapours released during evaporation and transpiration rises up and becomes cooler. At a sufficient height, the water vapours condense and change into tiny water droplets. So many tiny droplets come together to form the clouds.
Q.8 When does a drought occur?
Ans- When there is no rainfall or scanty rainfall for a long time, it results into a drought.
© www.vkscience.com