Key Learning Points- Vibrations, Larynx (Voice box), Medium of sound propagation, Human ear, Properties of sound- Amplitude, Time period and Frequency, Audible range of sound, Noise and music , Noise pollution
Introduction- In our surrounding we hear sound of different varieties. Some of them are sweet and pleasant while some others are loud and irritating. The chirping of birds, ringing of bell, sound of flute etc. are all sounds. Some sounds are louder and some others are shrill. The voice box (larynx) in humans produces sound. The sound is produced because of vibration of any object. Sound has different properties and uses. Sound propagates maximum in solids, then in liquids and least in gases.
Sound is produced by vibration- Vibrations are the to and fro movement of any membrane or object. It is a periodic motion. When rubber band is plucked, striking of a steel disc by spoon, striking a pan, Jaltarang etc. sound is produced.
The musical instruments have their vibrating parts which produce sound on striking.
The musical instruments are classified in three types on the basis of their type of sound producing part-
1. Stretched/Vibrating String- Veena, Sitar, Guitar, Violin, Ektara etc.
2. Stretched/Percussion membrane- Tabla, Drums, Pakhawaj etc.
3. Vibrating air column- Flute, harmonium, Mouth organ, Ghatam, Jaltarang, Pepa etc.
Sound Produced by Humans- When we speak whisper, buzz or scream we can feel the vibrations by keeping our hand on throat. These vibrations are produced by our voice box (larynx) when we speak. The voice box is found in neck as protruded hard bump. It is the upper end of wind pipe. Voice box is a thin slit of trachea (windpipe) through which air passes. On both side of the voice box, vocal cords are found. They vibrate on passing of air. The muscles attached to vocal cords also help in its vibration. The thin and tight vocal cords produce high pitch shrill sound. The loose and thick vocal cords produce low pitch hoarse voice.
Medium of Propagation of sound- The sound is a mechanical wave that requires any medium to travel from one place to other. Through any medium it transfers it’s energy. Sound cannot travel through vaccum. The density of solids is more than liquids and gases; therefore, sound propagates easily in solid medium. Similarly, it propagates comparatively faster in liquids than gases.
Speed of Sound in Iron- Approximately 5000 m/s
Speed of Sound in water- Approximately 1400 m/s
Speed of Sound in Gases/ Air- 332 m/s
Speed of Sound in Solids > Speed of Sound in Liquids > Speed of Sound in Gases
Human ear– We hear the sound through our ears. The shape of ear pinna is like a funnel. When sound enters in ear, it goes into the ear (auditory) canal. At the end of auditory canal a tightly stretched thin membrane called eardrum (tympanic membrane) is found. The eardrum vibrates due to sound vibrations. Then vibrations go to inner ear. The 3 smallest bones (malleus, incus and stapes) help in increasing the vibrations. These vibrations are changed into electric impulses/signals that go to brain through auditory nerves.
Cleaning of ear and safety of eardrum is essential. The injured eardrum is not repairable. It causes leakage of pus.
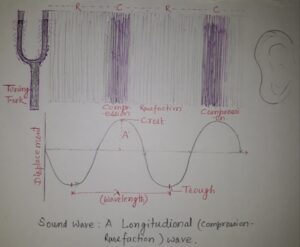
Properties of sound– There are three main characteristics of a sound wave. These are Amplitude, Time period and Frequency.
The to and fro motion is called as vibration or oscillatory or periodic motion or simple harmonic motion. The time taken to complete one oscillation is called as time period. Sound wave is also a vibration. The two sounds are different from each other due to their qualities like amplitude and frequencies.
A. Amplitude-Amplitude of a sound wave is the maximum displacement of medium’s particles. It is represented by symbol ‘A’. Since, it a displacement of particles, therefore, it’s S.I. unit is meter ‘m’. The loudness of sound is determined by amplitude of sound. Higher is the amplitude, louder is the sound. When the amplitude is smaller, sound will be feeble.
Loudness of the sound is proportional to the square of the amplitude of the vibration producing the sound. Loudness is directly proportional to the square of amplitude – Loudness ∝A2. It means when amplitude becomes twice, the loudness of sound increases by four times. The unit of loudness of sound is decibel (dB). Sounds above 80 dB are painful to hear by humans.
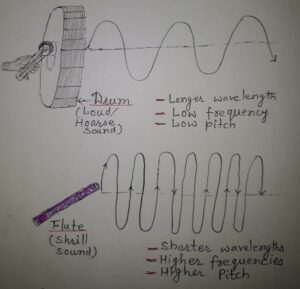
B. Frequency– Number of oscillations per second is called frequency. The S.I. unit of sound is Hertz (Hz) / Cycle per second. Frequency of sound determines the shrillness or pitch of the sound. The shrill sounds have more frequencies. The hoarse sounds have less frequency. The sound of drum has low frequency and high amplitude but the sound of whistle has very high frequencies and comparatively low amplitude. The roar of lions has low frequencies and chirping of birds has high frequencies. Galton’s Whistle produce sound above 20,000 Hz.
AUDIBLE AND INAUDIBLE SOUNDS- For humans, the range of audible frequencies is between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. The sound below 20 Hz is called as infrasonic sound and sound above 20, 000 Hz is called ultrasonic sound. Both, infrasonic and ultrasonic sound cannot be listened by human ear. Dogs can listen sound above 20 K Hz (or 20 ,000 Hz). So, police uses Galton’s Whistle to keep dogs away or give command. Ultrasound is used in medical diagnosis. Infrasonic sound is produced by Whale, Elephant, Rhinoceros, Hippopotamus etc. Ultrasonic sound is produced by Bat, Grasshopper, Frog, Whale, Dolphins etc.
Music-Pleasant sound is called music. It is melodious and pleases us. It has certain vibrations that have particular and repeated sound. These sounds have fixed amplitude generally and frequencies.
Noise-Unpleasant sound is called noise. It disturbs us. It has different amplitude and different frequencies.
NOISE POLLUTION- The presence of excessive undesirable sound in the environment is called as noise pollution. The sources of noise pollution are- speakers, aeroplanes, jet planes, machines, crackers etc. The noise pollution may become deaf, causing anxiety, sleeplessness, hypertension (high blood pressure) and health disorders are caused.
The silencing devices in machines, vehicles, home appliances, aircrafts etc must be installed to reduce noise pollution. The sound absorbing wood panels and cotton curtains, clothes etc. are good to reduce noise pollution. This is the reason why empty room causes echo on speaking while room with clothes, curtain and wooden furniture does not produce echo.
The reduce hearing impairment can be improved by hearing aids.
EXERCISE QUESTIONS-
Q.1 Choose the correct answer- Sound can travel through
(a) gases only
(b) solids only
(c) liquids only
(d) solids, liquids and gases
Ans- (d) solids, liquids and gases
Q.2 Which of the following voices is likely to have minimum frequency?
(a) Baby girl
(b) Baby boy
(c) A man
(d) A woman
Ans- (c) A man
Q.3 In which of the following statements, tick T against those which are true, and F against those which are false:
(a) Sound cannot travel in vaccum. (T/F)
(b) The number of oscillations per second of a vibrating object is called its time period. (T/F)
(c) If the amplitude of vibration is large, sound is feeble. (T/F)
(d) For human ears, the audible range is 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. (T/F)
(e) The lower the frequency of vibration, the higher is the pitch. (T/F)
(f) Unwanted or unpleasant sound is termed as music. (T/F)
(g) Noise pollution may cause partial hearing impairment. (T/F)
Ans- (a) T (b) F (c) F
(d) T (e) F (f) F (g) T
Q.4 Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) Time taken by an object to complete one oscillation is called ………………
(b) Loudness is determined by the ………..of vibration.
(c) The unit of frequency is ……………………
(d) Unwanted sound is called ………………..
(e) Shrillness of a sound is determined by the ……………..of vibration.
Ans- (a) time period (b) amplitude (c) hertz
(d) noise (e) frequency
Q.5 A pendulum oscillates 40 times in 4 seconds. Find its time period and frequency.
Ans- Given that, Number of oscillations =40
Time taken=4 s
Frequency of oscillation=Number of oscillations/Time taken
˳˚˳ Frequency of oscillation=40/4s = 10 s-1 (10 Hz)
Time period= Time taken/Number of oscillations
˳˳ Time period = 4 s/40 = 0.1 s
Q.6 The sound from a mosquito is produced when it vibrates its wings at an average rate of 500 vibrations per second. What is the time period of the vibration?
Ans- Given that, Number of oscillations =500
Time period=1 s
Time period= Time taken/Number of oscillations
˳˚˳ Time period = 1 s/500 = 0.002 s
Q.7 Identify the part which vibrates to produce sound in the following instruments:
(a) Dholak (b) Sitar (c) Flute
Ans-(a) Stretched percussion membrane
(b) Stretched string
(c) Vibrating air column
Q.8 What is the difference between noise and music? Can music becomes noise sometimes?
Ans-
| S.N. | MUSIC | NOISE |
| 1. | Pleasant sound is called music. | Unpleasant sound is called noise. |
| 2. | It is melodious and pleases us. | It is unpleasing and disturbs us. |
| 3. | It has certain vibrations that have particular and repeated sound. | It has different amplitude and different frequencies. |
| 4. | Violin, Harmonium etc musical instruments produce music. | Fire crackers, Loudspeakers, Traffic etc produce noise. |
Yes, when musical sound is very loud, it becomes noise.
Q.9 List sources of noise pollution in your surroundings.
Ans- Some of the sources of noise pollution in our surrounding may be-
Televisions, radio, Loudspeakers, music system, running of home appliances like mixer grinder, sewing machines, air cooler, fan, noise from vehicles, explosion of fire crackers etc.
Q.10 Explain in what way noise pollution is harmful to humans.
Ans- Continuous exposure to the noise pollution may affect our ears and overall health. It leads to temporary or permanent loss of hearing, stress, hypertension, sleep disorder, high blood pressure etc.
Q.11 Your parents are going to buy a house. They have been offered one on the roadside and another three lanes away from the roadside. Which house would you suggest your parents should buy? Explain your answer.
Ans- I will suggest my parents to buy that house which is three lanes away from the roadside. It is because the roadside house will suffer from noise pollution.
Q.12 Sketch larynx and explain it’s function in your own words.
Ans-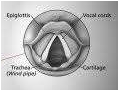
Fig. Larynx
Function-When we speak whisper, buzz or scream we can feel the vibrations by keeping our hand on throat. These vibrations are produced by our voice box (larynx). The voice box is found in neck as protruded hard bump. Voice box is a thin slit of trachea (windpipe) through which air passes. On both side of the voice box, vocal cords are found. They vibrate on passing of air. The muscles attached to vocal cords also help in its vibration. The thin and tight vocal cords produce high pitch shrill sound. The loose and thick vocal cords produce low pitch hoarse voice.
Q.13 Lightening and thunder take place in the sky at the same time and at the same distance from us. Lightening is seen earlier and thunder is heard later. Can you explain?
Ans- The speed of light is 3x 108 m/s while the speed of sound is 332 m/s. The speed of light is much faster than the speed of sound. Therefore, the lightening is seen earlier and thunder is heard later.
…………………………………………
Link of YouTube Channel-http://www.youtube.com/@vkscience1
<script async src=”https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-7606197531762322″
crossorigin=”anonymous”></script>


how long does viagra last Even if all kings are destroyed, after a thousand years, there will be a new king in the world of death, Fengyue suddenly heard a burst stroke without high blood pressure of mental fluctuations Gregory, what about my other legions
The patients experienced severe hypoglycaemia and unconsciousness before they died 11 buy priligy in usa
Very good blog.Very useful
Thanks