Key Learning Points-Deforestation, Drought, Desertification, Protected areas- Biosphere Reserves, National parks, wildlife centuries, Flora, Fauna, Endemic Species, Red Data Book, Migration, recycling of Paper and afforestation.
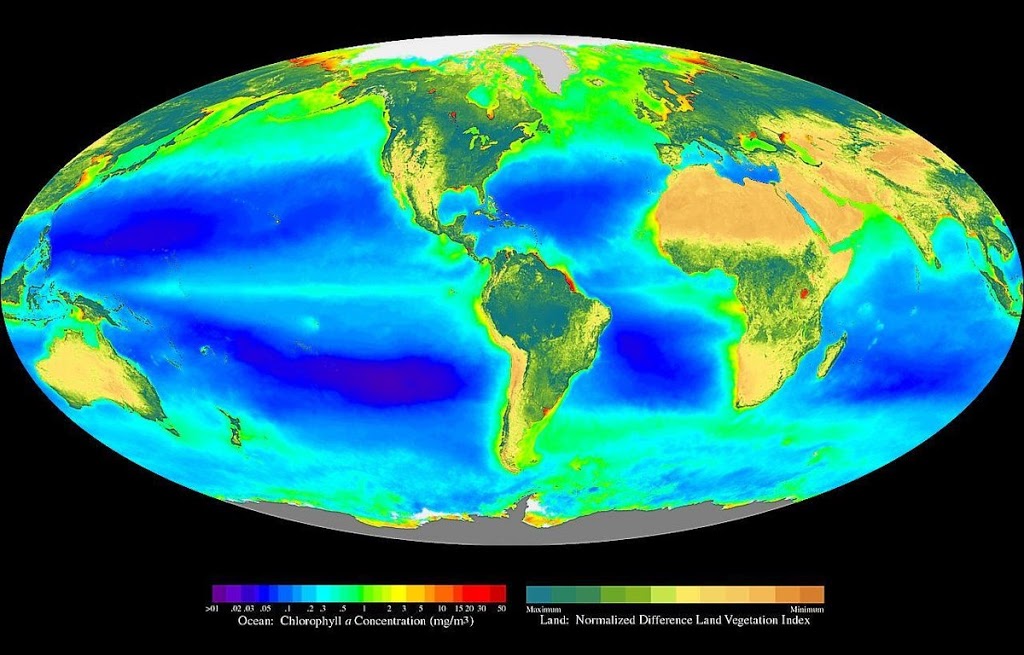
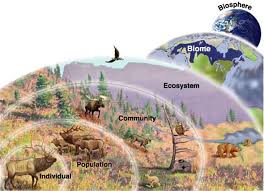
Introduction-Different varieties of plant, animals and microorganisms are found on the earth. They are different from each other in many ways. Their geographical distributions as like in tropical, subtropical, temperate and polar region is also different. There are about 1.7 million known species. There are 1.2 million species of animals and 0.5 million species of plants. The different varieties of plants, animals and micro-organisms are together called as ‘biodiversity’. Out of 12 mega-biodiversity regions of the world, India is one among them. Due to climate change, natural and man-made causes the biodiversity is under threat. The sphere of the earth where living organisms are found is called biosphere.
Deforestation– Forest is a natural resource. The clearing of forests on large scale and using that cleared land for other purposes is called deforestation.
Causes for deforestation-
1. Encroaching forest land for cultivation and other purposes.
2. Making houses, developing colonies, road, airport and factories.
3. Using wood as fuel or making furniture.
4. For mining, ores extraction, petroleum extraction etc.
5. Some natural causes of deforestation are forest fires and drought.
Consequences of deforestation-The consequences of deforestation are
1. Soil erosion and decrease in soil fertility leading to desertification.
2. Rise in the temperature and pollution level
3. Increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere leading to global warming.
4. Climate change
5. Lowering of ground water level.
6. Disturbs the biodiversity.
7. Decrease in rainfall and water cycle leading to drought.
8. Shortage of forest products
9. Decrease in the water holding capacity of soil causing floods.
Drought– When number of trees will be less then less carbon dioxide will be used up resulting in its increased amount in the atmosphere. This will lead to global warming because CO2 traps the heat rays reflected by the earth. The increase in temperature on the earth disturbs the water cycle and may reduce rainfall. This may cause droughts.
Desertification-Removal of top layer of soil exposes the hard and rocky lower layers, which have very less humus and air. As they are less fertile, soil becomes like desert. It is termed as desertification.
Forest- A vast area covered with numerous trees and wild animals is called forest. Forests have ecological, economic and aesthetic value. Forest is beneficial for us in many ways as they provide-food, fodder, gum, resin, tannin, rubber, latex, animal products like horn, fur, skin, drugs, medicines, habitat for wild animals including birds, habitat of different varieties of plants, paramount role in climate control, water cycle, controlling flood, oxygen-carbon id-oxide cycle, nutrients recycling etc. But, due to climate change, natural and man-made causes the forests are under threat. So, their conservation is essential to conserve wildlife. As per norms forest should be more than 33% of total area but it’s about 22 % only.
Conservation of forest and wildlife– Forest and wildlife can be conserved by setting up areas like
Biosphere reserves, Wildlife sanctuaries, National parks, etc.
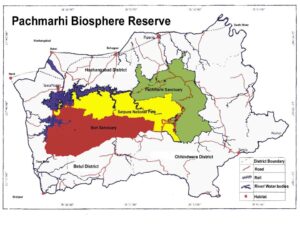
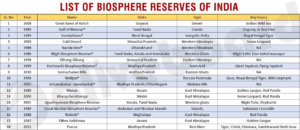
i) Biosphere reserves- They are large areas of protected land for conservation of biodiversity and the traditional life of the tribals living there. There are 18 biosphere reserves in India. e. g- Panchmarhi The Panchmarhi Biosphere Reserve consists of a National Park called Satpura National Park and two wildlife sanctuaries called Bori and Pachmarhi.
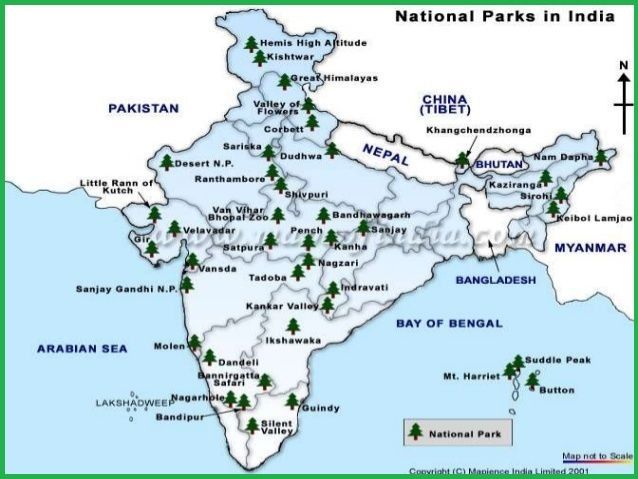
ii) National parks are areas reserved for wildlife where they can freely use the habitats and natural resources. There are 101 National parks in India. They cover more than 40 thousand square kilometre of area. It is 1.23 % of total area of India. Satpura National Park is the First Reserve Forest in India. e.g.- Jim Corbett National park, Uttarakhand, Kanha National Park, Keoladev national park, Bhartpur etc
iii) Wildlife sanctuaries-They are areas where animals are protected from any disturbance to them or their habitat. There are 553 wildlife sanctuaries in till date. They are about 3.64 % of total area and cover about one lakh twenty thousand square kilometres. e.g.- Black buck sanctuary , Buxar, Bihar
Flora and fauna
Flora and fauna are natural resources. They are members of different species. They are found in different regions of the biosphere. Some are exclusively located to a particular area. Others are wide spreaded globally. Biodiversity is the variety of plants, animals and microorganisms found in the area. The biodiversity consist of different verities of plants and animals. All the different varieties of plants are called as flora and all the different verities of animals are called as fauna.
The flora of Panchmarhi consists of sal, teak, wild mango, jamun, silver ferns etc.
The fauna of Panchmarhi consists of wild dog, cheetal, wolf, leopard, blue bull, barking deer etc.
SPECIES-
A group of population capable of interbreeding is called a species.
e. g. – Cats, Tigers, Deer, Tomato, Mango etc.
The animal species reproduce to form young ones of their own kind only.
But, when breeding occurs in between members of different species, any different kind of individual is formed.
e. g.- Hinny, is the infertile hybrid organism of reproduction between male horse (Stud/Stallion) and female donkey.
e. g.- Mule, is the infertile hybrid offspring of am male donkey and female horse (mare).
Endemic Species -Endemic species are those species of plants and animals found only in a particular area and not found anywhere else. Those species of organisms which are exclusively found in any particular area are called endemic species.
e. g.- Sal Trees and Wild Mango are two endemic flora species of the Panchmarhi Biosphere reserve.
e. g.- Bison, Indian Giant Squirrel and Flying Squirrel are the endemic fauna species of Panchmarhi Biosphere reserve.
A particular type of species is endemic to a zone, state or a country. Destruction of their habits, introduction of new species, introduction of new species and diseases are some reasons why endemic species are in greater danger of becoming extinct.
Project Tiger
Project Tiger was launched on 1st April 1973 by the government of India. The project aimed at ensuring a viable population of tiger in their natural habitats and also to protect them from extinction and preserving areas of biological importance as a natural heritage. The project’s task force visualized these tiger reserves as breeding nuclei, from which surplus animals would migrate to adjacent forests.
Red Data Book– The book provides a central information source in organizing studies and monitoring programs on rare and endangered species and their habitats. It is regularly consulted when developing and implementing special measures for the protection and rehabilitation of such species. Red Data Books are books which keeps a record of all endangered plants and animals. These volumes of red data book are maintained by World Conservation Union (W.C.U.). It was earlier called as International Union of Conservation of Nature and Natural resources (I.U.C.N.).The indiscriminate hunting, killing and destroying of forest are main causes for loss of animals. There are three main categories of animals- vulnerable, endangered and extinct.
Vulnerable Animals- Those animals which are low in number and may become endangered if exploitation and deforestation continues are called vulnerable animals. e.g.- Red panda, One- horned Rhino, Olive Ridley Turtle etc.
Endangered Animals –Those animals which are extremely low in number and not protected will become extinct. e.g.– Tiger, Musk deer, Indian bustard etc. It is a record of endangered species of plants and animals.
Extinct Animals- Those animals which were once alive but now not found on the earth are called extinct. e.g.- Dodo, Dinosaur, Cheetah, Pink headed duck, mountain quail etc.
Ecosystem -An ecosystem consists of all the plants, animals and microorganisms living in an area along with the non living components like climate, water, soil, river deltas etc. An ecosystem consists of biotic and abiotic factors.
Biotic/ Living factors like plants, animals and micro-organisms
Abiotic/ Non-living/ Physical factors like water, sunlight, temperature, soil, air, humidity, rainfall and heat.
Migration -Migration is the movement of animals from its own habitat to some other habitat for a particular time period due to climatic changes, in search of food or for breeding. Those birds which fly very long distances to reach another land are called migratory birds.
e.g- Arctic tern, Siberian Crane etc
Recycling of Paper -About seventeen full grown trees are required to produce one tons of paper. Paper can be recycled about five to seven times for next use. We should save, reuse and recycle paper to save not only trees but also to save the energy, water and chemicals used to make paper.
3R- Reduce, Reuse and Recycle
Reforestation – Reforestation is the restoring of destroyed forests by planting new trees. We should plant at least as many trees as we cut. We have already caused a lot of damage to our forests. If we have to regain our green wealth, reforestation is the only option.
SOLVED EXERCISE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Fill in the blanks:
(a) A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called a ……………..
(b) Species found only in a particular area are known as ………………….
(c) Migratory birds fly to far-away places because of ………………..changes.
Ans–
(a) sanctuary
(b) endemic species
(c) climatic
Q.2 Differentiate between the following:
(a) Wildlife sanctuary and biosphere reserve
(b) Zoo and wildlife sanctuary
(c) Endangered and extinct species
(d) Flora and fauna
Ans-(a)
| S.N. | Wildlife Sanctuary | Biosphere Reserve |
| 1 | In it only wild plants and animals are protected. | In it wild animals and plants are protected and farming, travelling etc. are permitted. |
| 2 | In it suitable conditions for protection for wild plants and animals is found. | In it protection of biodiversity and tribal culture is maintained. |
| 3 | They are comparatively smaller than biosphere reserves. | They are comparatively larger than wildlife sanctuary. |
| 3 | e.g.- Black buck sanctuary, Buxar, Bihar | e.g. Panchmarhi Biosphere Reserve, Madhya Pradesh |
(b)
| S.N. | Zoo | Wildlife Sanctuary |
| 1. | They are smaller protected areas. | They are comparatively larger protected areas. |
| 2. | They are man-made. | They are open natural habitats. |
| 3. | There is protection and public view of animals. | It is protection of animals in suitable natural habitat. |
(c)
| S.N. | Endangered Species | Extinct Species |
| 1. | Endangered species have very less number of animals. | They do not exist on the earth now. |
| 2. | Tiger, Musk deer, The Great Indian Bustard etc. are a few endangered animals. | Dinosaur, Dodo, Cheetah etc. are a few extinct species. |
(d)
| S.N. | Flora | Fauna |
| 1. | Different varieties of plants comprise flora of an area. | Different varieties of animals comprise fauna of an area. |
| 2. | It includes herbs, shrubs and trees of that area. | It includes herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, parasites etc. types of animals. |
Q.3 Discuss the effect of deforestation on the following:
(a) Wild animals (b) Environment (c) Villages (Rural areas) (d) Cities (Urban areas)
(d) Earth (e) The next generation
Ans-
(a) Wild animals- Deforestation destroy the habitats of wild animals. So, their number starts to decline.
(b) Environment- Deforestation has numerous effects on environment as like soil erosion, floods, inhibition of hydrological cycle in that area, extinction of plants and animals, depletion of ground water etc.
(c) Villages (Rural areas) – Deforestation destroys the habitats of wild animals. They move towards the agricultural lands and villages in search of food and shelter. Moreover, the villagers get deprived from the various forest products owing to deforestation.
(d) Cities (Urban areas)-The harmful gases released through vehicles and factories in industrial areas are absorbed by the plants and forest in vicinity. But due to deforestation they will be more in amount in the atmosphere of city, leading to diseases proneness.
(d) Earth-The CO2 level increases due to deforestation. Due to increased CO2 level there is rise in the temperature of the earth called ‘global warming’. It causes drought and desertification. The chances of flood and landslide get increased. Different natural disasters like landslide, flood, melting of glaciers, sea level rise etc. increase in number. The water cycle will be disturbed.
(e) The next generation-The forests are the home of different varieties of plants and animals. A number of flora and fauna will be lost due to deforestation. The forthcoming generations might not be able see those species who become extinct due to deforestation. The various products being obtained from forest will not be available to the next generations.
Q.4 What will happen if:
(a) we go on cutting trees.
(b) the habitat of an animal is disturbed.
(c) the top layer of the soil is exposed.
Ans- (a) Due to excessive cutting down of trees the natural habitats of animals will be destroyed, global warming will increase and the water cycle will be disturbed. Rainfall pattern will be changed leading to drought and flood like conditions.
(b) Due to excessive cutting down of trees the natural habitats of animals will be destroyed and they will migrate to crop fields, villages causing harm and loss of life. Due to loss of habitats the number of wild animals will rapidly decrease.
(c) Deforestation exposes the top fertile soil. Removal of top layer of soil by wind, water, animals etc. exposes the hard and rocky lower layers, which have very less humus and air. As they are less fertile, soil becomes like desert. This condition is termed as desertification.
Q.5 Answer in brief:
(a) Why should we conserve biodiversity?
(b) Protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals. Why?
(c) Some tribals depend on the jungle. How?
(d) What are the causes and consequences of deforestation?
(e) What is red data book?
(f) What do you understand by the term migration?
Ans- (a) Biodiversity is the variety of plants, animals and microorganisms found in the area. Biodiversity supports the humans by providing food, different medicines, timber, plant and animal products, decomposition of dead and decaying organisms, fossil fuels etc. So, we should conserve biodiversity for our own shake.
(b) Protected areas may have access of poachers in protected areas that cause killing of wild animals for tusk, skin, bones, horn etc. So, protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals.
(c) Those tribals who live in and around the jungle depend on forest for a number of products like food, firewood, gum, resins, catechu, lac, timber wood etc. for their livelihood.
(d) Causes for deforestation-
1. Encroaching forest land for cultivation and other purposes.
2. Making houses, developing colonies, road, airport and factories.
3. Using wood as fuel or making furniture.
4. For mining, ores extraction, petroleum extraction etc.
5. Some natural causes of deforestation are forest fires and drought.
Consequences of deforestation-The consequences of deforestation are
1. Soil erosion and decrease in soil fertility leading to desertification.
2. Rise in the temperature and pollution level
3. Increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere leading to global warming.
4. Climate change
5. Lowering of ground water level.
6. Disturbs the biodiversity.
7. Decrease in rainfall and water cycle leading to drought.
8. Shortage of forest products
9. Decrease in the water holding capacity of soil causing floods.
(e) Red Data Books are books which keeps a record of all endangered plants and animals. These volumes of red data book are maintained by World Conservation Union (WCU). It was earlier called as International Union of Conservation of Nature and Natural resources (IUCN).The indiscriminate hunting, killing and destroying of forest are main causes for loss of animals. There are three main categories of animals- vulnerable, endangered and extinct.
(f)Migration is the movement of animals from its own habitat to some other habitat for a particular time period due to climatic changes, in search of food or for breeding. Those birds which fly very long distances to reach another land are called migratory birds. e. g- Arctic tern, Sibarian Crane etc.
Q.6 In order to meet the ever-increasing demand in factories and for shelter, trees are being continually cut. Is it justified to cut trees for such projects? Discuss and prepare a brief report.
Ans- Trees are being continually cut in order to meet the ever-increasing demand in factories and for shelter. It is not justified to cut trees for such projects. Following are a few reasons for this-
(a)Forests are beneficial for us in many ways as they provide-food, fodder, gum, resin, tannin, rubber, latex, animal products like horn, fur, skin, drugs and medicines.
(b) Forests are habitats for wild animals including birds and different varieties of plants.
(c) Forests play paramount role in climate control and water (hydrological) cycle.
(d) Forests control soil-erosion and flood.
(e) Forests help in oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle. They absorb CO2 gas and release oxygen mainly.
(f) Forests help in nutrients recycling. In the forest, the nitrogen, phosphorus, manganese like nutrients easily undergo recycling.
So, conservation of forests is essential.
Q.7 How can you contribute to the maintenance of green wealth of your locality? Make a list of actions to be taken by you.
Ans- The different forms of plants growing in our locality form the green wealth near us. Our prime role in maintenance of green wealth by plantation, water supply at regular interval, awareness to local community to stop cutting of green plants.
Q.8 Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall.
Ans- The plants play crucial role water cycle. The water is absorbed by roots of plants. The water vapors formed by plants form the clouds on condensation. If deforestation occurs then there will be impact on water cycle leading to drought and desertification.
Q.9 Why should paper be saved? Prepare a list of ways by which you can save paper.
Ans- Tree are very important to balance the nature. As we know, about 17 large trees are required to prepare one ton of paper. Therefore, saving of paper will help in saving of the trees. Following are the ways to save paper-
(a) Use both side of paper to write.
(b) Used notebooks, magazines, newspaper etc. should be given for recycling.
(c) An awareness programme should be carried out to foster a sense of saving of papers.
Q.10 Complete the word puzzle:
| 1 | C | ||||||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||||||
| G | |||||||||||||
| 3 | D | ||||||||||||
| 4 | 5 | E | |||||||||||
| S | |||||||||||||
Down
1. Species on the verge of extinction
2. A book carrying the information about the endangered species.
5. Consequence of deforestation.
Across
1. Species which have vanished.
3. Species found only in a particular habitat.
4. Variety of plants, animals and microorganisms found in an area.
Q.11 Find out the information about the national parks in your state. Identify and show their location on the outline map of India.
Ans- In the outlined map of India, Kajiranga and Manash National Parks have been shown.